“AI security” describes the security risks and possibilities related to Artificial Intelligence.
People have been working with AI security for many years. However, thanks to the rise of generative AI, the problems and opportunities have exploded. Although many people are excited about using AI, we must remember that it brings many issues.
Fortunately, many agencies are working hard to understand how to use AI securely and how to use AI to create better security systems.
This article will introduce this difficult topic – focussing on risk reduction. It will explain:
- the meaning of “AI security” (in detail);
- the main risks of poor AI security;
- The steps to improve AI security.
Security risks have been on business leaders’ minds in the past few years. With the rise of the digital workplace and its benefits, we’ve also seen many new security challenges. AI is yet another way for security vulnerabilities to enter your systems – so let’s look at how to improve everything.
What does AI security mean?
“AI security” is a catch-all expression for the relationship between AI and security. Although we are focussing on the negative elements in this article, “AI Security” includes the risks and the opportunities for AI.
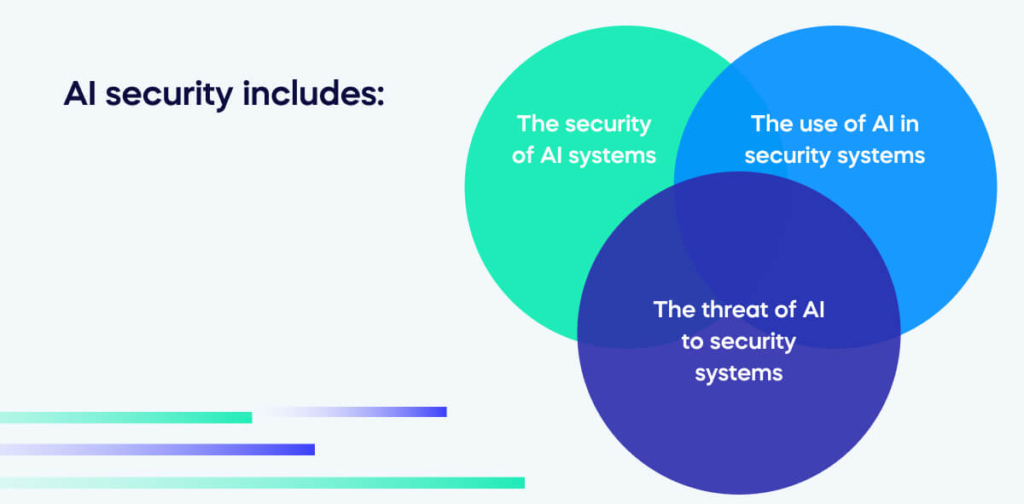
AI security includes:
- The security of AI systems. Is your LLM safe from attacks? If someone inputs confidential information, will it remain safe? Within your business, are people using AI technology in approved ways?
- The use of AI in security systems. Can AI be effectively mobilized in security systems?
- The threat of AI to security systems. How will your online data be protected from malicious AI attacks? Do you have adequate cyber defense to prevent AI intrusions?
Just as people are wising up to the opportunities of AI, leaders are also starting to see how these technologies could create a lot of problems within their organizations.
If we don’t pay attention to AI security now, it will only worsen. A 2022 McKinsey forecast reflected that AI would embolden hackers in particular: “Over the next several years, they will be able to expedite—from weeks to days or hours—the end-to-end attack life cycle, from reconnaissance through exploitation.”
Whatever the nature of the attack, you can’t afford to take any chances. So, let’s take a look at some of the major risks.
The risks of poor AI security
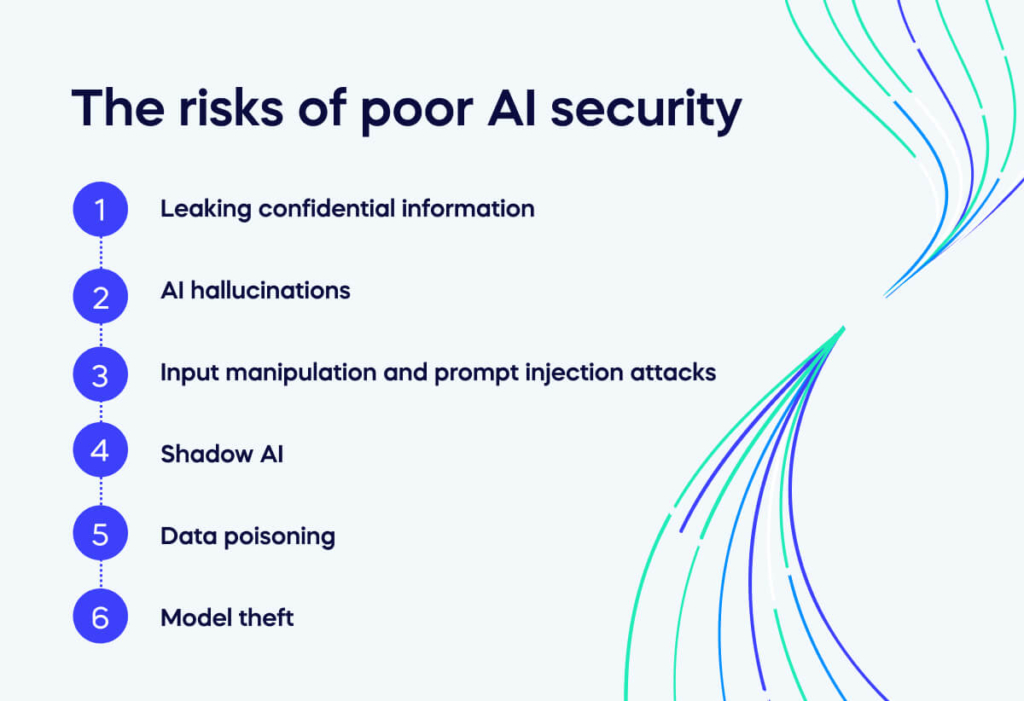
AI security is not just one issue: using AI brings many security risks. This section will briefly introduce some of the main AI security problems. Some of these problems will be more relevant for your organization than others. You can use this list for an initial assessment of your needs.
Some of the major problems in AI technologies include:
- Leaking confidential information. With all of generative AI’s amazing capabilities, it’s tempting to trust the chat box with all kinds of sensitive data. This is a bad idea, as the LLMs behind most AI chatbots use that input as training data. If your employees use AI tools carelessly, they may give away important secrets about your company or clients.
- AI hallucinations. By now, we’re all familiar with the nonsense that AI models sometimes produce. ChatGPT will happily fabricate a completely false answer if it doesn’t know something. That’s fine if you’re just having fun. But if you rely on AI output for your business dealings, you’re opening the door to a world of pain. And by the time you realize it, it might already be too late.
- Input manipulation and prompt injection attacks. This is a cyber threat within the models themselves at the top of the AI supply chain. Cyber attackers use the input prompts to trick the model into generating biased, harmful, or unintended content. By exploiting vulnerability in prompt-based AI systems, attackers can spread misinformation, hate speech, or malicious content, undermining the model’s reliability and trustworthiness. Fortunately, experts are discovering more ways to protect AI systems from this manipulation.
- Shadow AI. The new term Shadow AI refers to the use of unauthorized AI systems by employees. When staff members independently find a way for an AI system to make their work faster – they are probably not thinking about the security threats they are opening up. Shadow AI is especially challenging because no one understands the limitations of Generative AI capabilities. Until we do, some IT leaders may temporarily ban AI software within their companies.
- Data poisoning involves introducing malicious or misleading data during the training process. This can compromise the model’s performance, leading to inaccurate predictions or security vulnerabilities. Attackers can manipulate AI systems, making them less reliable and potentially causing real-world harm or exploitation.
- Model theft. This is another problem for the artificial intelligence systems themselves. It is a critical concern in AI security because it involves unauthorized access to and duplication of proprietary machine learning models. Malicious actors can steal these models to avoid the time and cost of development, potentially using them for malicious purposes or financial gain. This theft can erode a company’s competitive advantage, jeopardize intellectual property, and undermine trust in AI systems.
AI security is still a relatively small part of the puzzle in the big picture of digital business infrastructure. Even in April 2023, AI was hardly mentioned in Gartner’s top cybersecurity risks for the year. Even if AI is just one area among many risks, it’s still important for people to address AI-specific security measures as part of their wider security programs.
The steps for improving security in your business AI systems
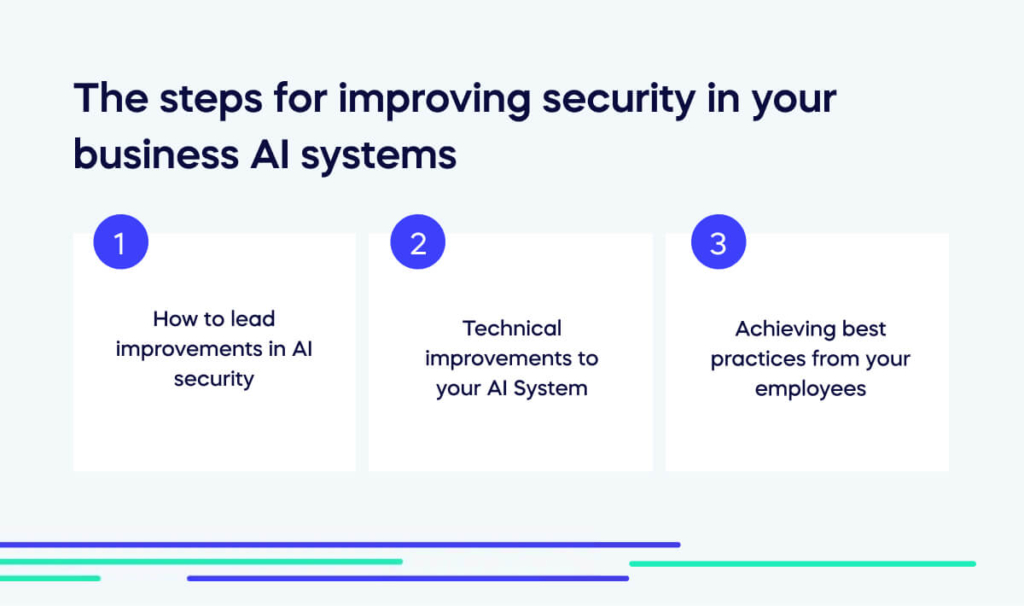
So – how do we solve the problem of AI security? The IT world is still developing the best answers. However, we can already see that improving AI security takes good leadership, technical developments, and sensitive staff training. So, let’s see how this works.
How to lead improvements in AI security
Simply put, leaders have to take responsibility for potential security threats. The personnel involved will be different at every company. But the conversations about AI risk need to start soon.
Often, you will need to include surprising new policies into your leadership. For example, any company working closely with technology should introduce a policy for bringing “Shadow AI” into your general business architecture. If you’ve got a budding prompt engineer on your team, you need to know the right checks and balances have been made prior to a roll-out.
Technical improvements to your AI System
The technological solutions for AI risks are slowly emerging. Some of the techniques you can apply include:
- Establish a robust security foundation for AI, drawing parallels with existing threats to software and data.
- Implement advanced detection mechanisms and response protocols to address potential malicious AI activities.
- Automate defensive measures to promptly mitigate AI-related attacks and vulnerabilities.
- Implement organization-wide security controls at the platform level to ensure comprehensive protection.
- Foster agility by conducting frequent testing, responding effectively to crises, and staying adaptable to emerging threats.
- Gain a deep understanding of your organization’s AI usage patterns to identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
Achieving best practices from your employees
Finally, make sure that your staff is well-prepared for the challenges of cyber threats. Don’t let human error be the main weakness in generative AI systems! As we’ve said above, you may need to restrict access to AI within your workplace – this doesn’t feel great, but it might be necessary.
Appropriate training in the main software systems and security operations could make a major difference. When staff are more knowledgeable about the risks of cyber attacks, complacent AI misuse, and human error, they will have actionable insights to change their behavior.
Artificial Intelligence: problems with solutions
The world is quickly discovering the best and worst of AI. The digital learning curve for these products is remarkably quick, but with security hazards that most users don’t understand.
The major technology companies are catching up – providing organizations with the defense strategies they need to avoid the potentially severe consequences. IBM, Google’s SAIF, and even research institutions like MIT are all taking the lead that the digital world requires.


