Organizations are rapidly adapting to generative AI. They are addressing high employee turnover during the Great Resignation and are still adjusting to remote and hybrid work due to the global pandemic.
At its core is the recognition that change is essential for progress and maintaining relevance. Failure to adapt to evolving conditions risks stagnation.
Business readiness is key to managing change. It involves assessing the company’s current state and identifying gaps. It also considers implementing change management strategies to bridge those gaps. This enables the company to embrace future changes.
This article explores business readiness and its importance. It explains who prepares a company for change and outlines the essential steps to achieve business readiness. We’ll provide guidance on implementing a business readiness management framework to enhance organizations’ ability to handle change in an evolving environment.
What is business readiness?
Business readiness is a strategic process that helps organizations navigate, anticipate, and respond to changing market conditions. It can also help you react to industry trends and technological advancements. Business readiness aims to build adaptability and resilience into the organization. This approach goes beyond reacting to change. Instead, it seeks to embed these qualities into the organization’s core.
Business readiness management connects business operations and project initiatives. It identifies essential steps needed before launching a project or strategy. It also monitors progress until completion. This ensures smooth collaboration and alignment of objectives.
At its core, business readiness recognizes that change is inevitable. Leaders must embrace it and develop a clear vision and mission supported by well-defined objectives. This approach helps businesses address challenges and seize opportunities.
McKinsey supports this. It highlights that “business leaders need to focus on the ‘superpowers’ of speed, technology, talent, and leadership.”
Why is business readiness important?
Business readiness is important because it helps organizations handle change and tackle challenges. Business operations are becoming more complex and unpredictable. The need for change usually comes from urgent internal or external factors.
Forbes asserts that “Change capability is the most important missing contemporary for today’s leaders.” Additional research also shows that 77% of senior executives believe that their inability to adopt change management will impact their ability to stay competitive in the marketplace.
Business readiness goes beyond regular change management. It encourages a proactive mindset in organizations, helping them foresee obstacles and seize new opportunities. It also builds a culture of innovation and flexibility.
By prioritizing business readiness, companies become more resilient and agile. This enables them to handle disruptions better and navigate change with greater ease.
What is the difference between business readiness vs. change management?

The main difference between business readiness and change management is their focus. Business readiness prepares a business for upcoming changes. It ensures smooth transitions and business continuity. It assesses readiness levels and sets up necessary protocols and resources.
However, change management handles the actual process of implementing changes within an organization. It deals with the human and procedural aspects of change and guides employees and the organization through the transition.
Who helps the organization prepare for change?
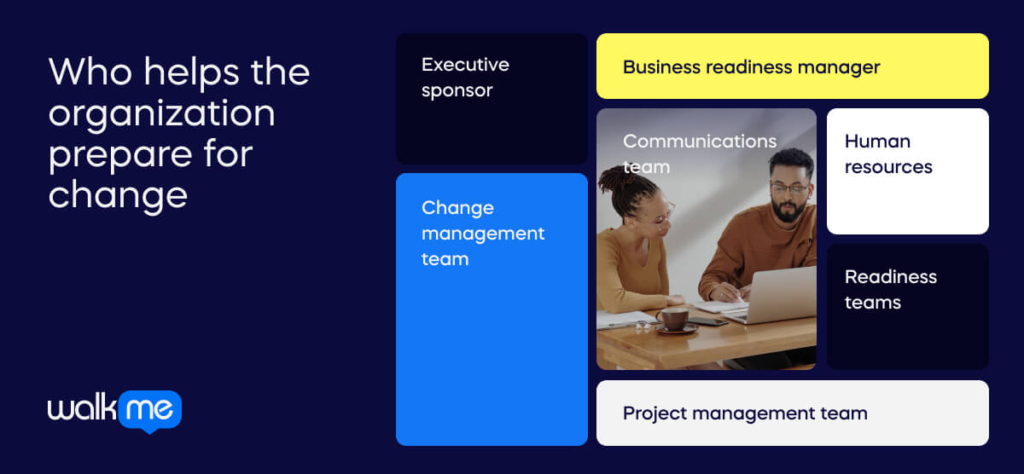
Preparing an organization for change and achieving business readiness requires assigning several key roles. These individuals collaborate to ensure the effective implementation of new initiatives.
Executive sponsor
A high-ranking executive who champions the change initiative. They provide strategic direction. They also ensure that there are necessary resources for a successful transition.
Business readiness manager
The business readiness manager oversees the entire readiness process. They coordinate efforts among various teams and track progress. They also ensure the business meets all prerequisites before moving forward.
Readiness teams
These teams include representatives from different departments. They identify potential challenges, develop solutions, and ease organizational communication. Members include subject matter experts, process owners, and frontline employees.
Change management team
This team plans and executes the change management strategy. It provides training to address employee concerns and can also track the adoption of new processes and systems.
Project management team
This team is tasked with overseeing the technical aspects of the change initiative and ensures you deliver projects on time. They also need to be within budget and aligned with strategic objectives. A Gartner survey reveals that nearly 70% of PMO and PPM leaders think the volume, frequency, and complexity of change have grown compared to three years ago.
Human resources
HR supports employees throughout the change process. They provide guidance on workforce planning, talent development, and performance management.
Communications team
This team crafts clear and consistent messaging during times of change. They can inform and engage all stakeholders throughout the transition.
Organizations can establish a strong support system by identifying and assigning these key roles. This system enables them to navigate change and achieve business readiness.
How to implement a business readiness management framework

Throughout this article, we have underscored the significance of business readiness. It is a systematic approach that prepares organizations for change. It also ensures the success of new projects.
Now, let’s delve deeper into the business readiness management framework. By following these crucial steps, companies can reduce risks and streamline implementation, enhancing the likelihood of meeting their objectives.
- Create your readiness group of champions
Establishing a cross-functional readiness group is essential within an organization. This stakeholder group should include representatives from different departments and levels. The group ensures a better assessment of potential challenges and opportunities.
They create a detailed plan outlining steps, resources, and timelines for achieving business readiness. It will also cover employee engagement, communication strategies, change management, and employee training.
- Engage in scenario planning and stress testing
After forming the plan, the team should consider potential scenarios for issues. They should then plan mitigations and workarounds for any problems. It is beneficial to involve operational management and the eventual owners of the new service at this stage.
Stress testing involves subjecting the project and systems to simulated high-demand scenarios. You can do this to identify vulnerabilities and confirm the organization’s capacity to handle unexpected challenges.
- Test before going live
Contingency planning entails creating alternative strategies and response mechanisms to reduce risks and address unforeseen circumstances. Conduct trials to test the project’s components. These include new processes, technologies, or systems in real or simulated environments.
Pilot the change project in a controlled subset of the organization. Or with a small set of customers before going live. These trials provide valuable insights, allowing for fine-tuning, issue identification, and feedback gathering.
- Train following your pilot
Training colleagues and informing them about upcoming changes will be necessary. Schedule training sessions with subject experts before the change event. Ensure adequate coverage for those unable to attend and brief teams on the new processes.
Clear and concise communication is essential. This can outline changes, impact timelines, workarounds, and key contacts for escalations. It can also provide supporting materials like video recordings and documentation. Hands-on practice with the new tools or processes is also crucial.
- Reduce disruptions during implementation
Business continuity planning is critical in ensuring uninterrupted operations and reducing disruptions during project implementation. Develop strategies, procedures, and safeguards and test these plans during trials. This will ensure plans are effective before going live and prepare for unexpected events.
- Have checklists to assess progress
Incorporate go/no-go checklists and stage gates to ensure meticulous decision-making and progress tracking. These checkpoints establish clear criteria. It can also check parameters to determine readiness for each project phase. Stage gates serve as decision points for assessing progress. It also allows for adjustments, reassessments, or project halts if necessary.
- Implement your framework
Execute the business readiness framework. Track progress and adjust the approach as necessary. You can do this to address emerging challenges or capitalize on unforeseen opportunities.
Communicate updates to stakeholders. This ensures transparency and maintains momentum throughout the project lifecycle.
- Consider what could go wrong on the day
Several tactics can ensure a smooth transition when your change goes live. Create an hour-by-hour plan or run book that tracks all activities. Establish communication channels such as radio, mobile phone groups, and CCTV live feeds.
Deploy change agents, including project and operational staff, to support and report issues. Provide remote support through helplines and help chats. Establish a command and control center with representatives for quick issue resolution. Put in place a meeting cadence for progress updates and quick escalation processes to manage dependencies.
- Evaluate success
Upon project completion, assess whether you have met all the desired outcomes. Conduct a post-implementation review to identify lessons learned. You should also celebrate successes and apply insights to future initiatives.
Adhering to this business readiness management framework can help organizations prepare for change. It can also foster an environment for the execution of new projects.
Business readiness management checklist
A business readiness checklist helps prepare for organizational changes. It covers key areas like change strategy, communications, training, support, and documentation. It includes questions about identifying stakeholders and their roles.
It ensures the change aligns with organizational goals. The checklist helps lead people through the change and evaluates stakeholder support. It also addresses managing resistance.
Additionally, it asks about key messages and audiences. It identifies training needs and timelines, along with support resources. It determines documentation requirements. This checklist guides thorough planning to ensure successful implementation of changes.
Here are some of the questions and areas that you should consider when creating one:
Change strategy
Do you have executive sponsorship?
Have you defined roles and responsibilities?
Will you need change agents to drive implementation?
Have you completed a stakeholder analysis?
Which staff group does the change affect?
Does this change conflict with other workplace priorities?
How will you lead your employees through this change?
What training and support will you offer?
How will you assess who is on board with the change?
How involved are your employees in assessing the effect of the change?
How will you deal with resistance to change?
Environment or existing infrastructure
Has anyone on our team raised flags about the environment’s operational readiness?
If fixes are still needed, what is a reasonable timeline for incorporating them?
Have we tested this outside our development environment and within the user environment?
What are the existing tools that staff already use? Can these help with the change?
Communication
How will you communicate the main messages about the change?
How often and through which channels?
Who is the main audience for this change?
Why should they care about this change, and how will it make a difference for them?
What are you trying to do with this change? A behavior change? A change in responsibilities?
Do you need to prepare any communication materials?
When do you need to distribute them?
What obstacles do you need to overcome by communicating?
How will you measure whether your communications are successful? Surveys? Focus groups?
Do our staff know the communication channels for reporting errors?
Training for end users
Who is the main audience that you need to train?
How many people do you need to train for the change?
Will the training be optional or compulsory?
Have you identified any specific training needs for the change depending on the department?
Have we created training materials for our users?
Are there features associated with the change that aren’t covered in these materials?
Do you have any training constraints like the change timeline?
Who will create and deliver the training?
Will you use a digital adoption tool to roll out training?
What specific training strategies will you use for this change? Cross-training, e-learning, leadership development training?
Risk assessment
What is the likelihood you won’t be able to implement the change by the required deadline?
How can you focus on features?
How would you roll out more updates as and when you are able?
Will you have enough staff on the help desk for launch day to respond to employee questions?
How can you triage employee issues to speed up response times?
Do some elements of the change have different user capacity levels than others?
Do those differences make sense, or should we update them before launch?
Support team
Who will support staff through and after implementation?
How long will you need a support team to do this?
How will you assess whether the support team is needed for longer?
Do you have a backup plan if employees need more help adjusting to the change?
Documentation/training materials
What type of materials will each department need to help them through the change?
Do staff need new job aids?
Is there a need for an FAQ guide or user guide to answer simple queries?
Who will create these materials?
Do you need to outsource this task?
How will you distribute these materials, and when?
Embracing change for business readiness
In conclusion, business readiness transcends preparing for change. It involves nurturing resilience and fostering collaboration. It empowers employees to become catalysts of enterprise transformation within the organization. If a company is unprepared for change, it risks falling behind or becoming obsolete.
Achieving business readiness involves overcoming several key challenges. These can hinder an organization’s ability to adapt and thrive.
Resistance to change among employees is common. Overcoming this requires effective change management goals and clear communication. It also considers involving staff in the change process. Resource constraints, such as limited budget, staff, or technology, can hinder readiness efforts. Organizations must focus on needs and divide resources well.
Aligning goals across all departments and stakeholders can be challenging. Misalignment can lead to conflicts and inefficiencies. Managing the difficulties of organizational changes requires meticulous planning and skilled project management.
Communicate effectively, consistently, and transparently with employees. This communication must clarify the need for change, expected outcomes, and individual roles. Additionally, organizations must be agile and responsive to external factors, such as market volatility, technological advancements, or regulatory changes.
Addressing these challenges head-on is essential. Implementing a business readiness framework is a dynamic and iterative process. It requires strategic planning, agile execution, vigilant monitoring, and effective communication.

