Companies considering app modernization, which can include updating aging servers or potentially unreliable firewall appliances, are increasingly turning to cloud computing to reap its advantages.
Consequently, numerous organizations are initiating a partial transition to the cloud. A cloud migration strategy encompasses a comprehensive plan for relocating a company’s digital assets, services, databases, IT resources, and applications, either in part or entirely, to cloud-based environments. Additionally, cloud migration may encompass transferring from one cloud provider to another.
Given the critical role that cloud migration plays in achieving real-time and optimized performance and efficiency, it is important to conduct a full analysis of existing tools, devise a well-structured plan, and execute it meticulously to ensure the cloud solution aligns seamlessly with your business requirements.
By the end of this article, you will understand:
- What a cloud migration strategy is, and why you need one
- The various types of cloud migration strategies
- The benefits and challenges associated with cloud migration
- A step-by-step guide for successfully implementing a cloud migration strategy within your business
What is a cloud migration strategy?
A cloud migration strategy is a blueprint for systematically transferring digital assets, applications, and services from on-premises infrastructure to a cloud computing environment. Adopting such a cloud transformation strategy facilitates the identification and execution of the most efficient, least disruptive, and cost-effective conversion from on-premises to the cloud.
When the time comes to transition from an on-premises setup to the cloud, a well-crafted cloud migration strategy becomes invaluable for your organization. To minimize disruptions, this strategy should be customized to align with your specific business needs and existing environment, considering any dependencies or potential challenges that could impede a successful migration.
Why do you require a cloud migration strategy for your business?

There are several reasons why a business could adopt a cloud migration strategy.
These reasons include:
Reducing costs
Migrating to the cloud can be more cost-effective than maintaining in-house servers due to the pay-as-you-go model. However, initial costs must be considered, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) fees, resource transfer expenses, employee training, and running parallel on-premise and cloud setups for continuity. Despite these initial investments, cloud infrastructure often proves cheaper in the long term, especially after deciding which components to retain, refactor, or retire.
To make existing workloads easier
The specific needs and maturity of the applications being migrated are crucial. Applications demanding high performance, low latency, or high availability require a cloud provider that can meet these needs with minimal disruption. A detailed analysis of each application’s readiness and a well-aligned migration strategy with clear goals and risk management plans are essential.
To adhere to security and compliance needs
Migration involves transferring large volumes of data, posing security risks. Enterprises must establish new access controls and consider encryption for data in transit or physical security for data transmitted via hard disks. Compliance with regulations like GDPR is also critical. Strategies include keeping sensitive data on-premise or choosing cloud providers with specific server locations for compliance.
Permits alignment with business objectives
Goals such as cost reduction, scalability, and agility significantly impact the choice of cloud migration strategy. Enterprises must align the architecture and needs of each workload, skill, timeframe, and budget with these objectives.
Allows the company to maintain its competitive stance in the future
The rapid pace of technological advancement makes on-premise infrastructure quickly outdated. Cloud environments, provided by IaaS vendors, continually update to the latest technology, allowing organizations to test new solutions without significant upfront investment. The cloud supports innovation and agility, which is crucial for staying competitive.
Improves interoperability
Today’s users access services from multiple devices, necessitating flexible and scalable solutions. If interoperability and agility are primary goals, refactoring code to interface with various cloud services and applications is vital.
Types of cloud migration strategies
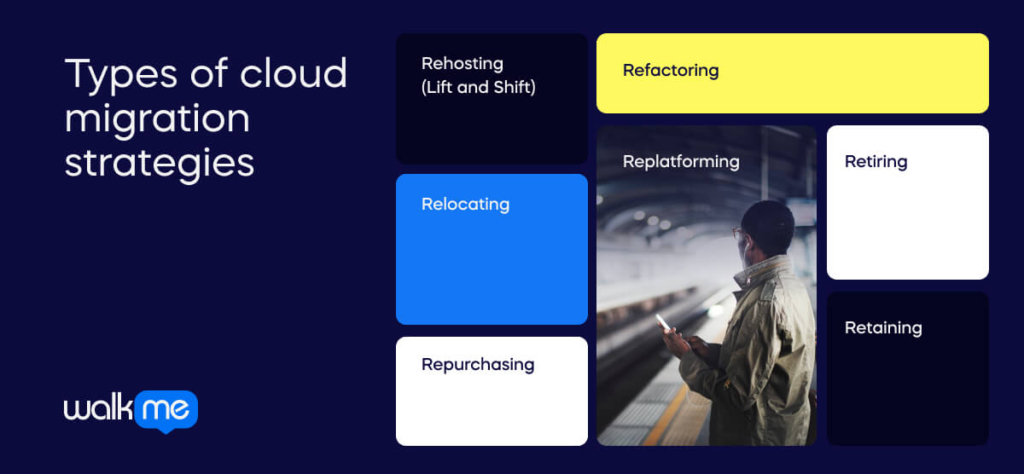
There are seven key strategies for seamless cloud migration: rehosting, relocating, repurchasing, refactoring, re-platforming, retiring, and retaining. Initially termed the “5 Rs” by Gartner, AWS later expanded these to the “7 Rs.” Each strategy is tailored to meet specific organizational needs during cloud migration:
Rehosting (Lift and Shift)
This involves transferring your existing setup from on-premises to the cloud without significant modifications. It’s suitable for organizations seeking quick ROI and those who need more time to leverage advanced cloud features. This approach is particularly effective for businesses aiming to accelerate their cloud migration cost-effectively, with plans to implement additional modifications.
Relocating
This strategy allows for migrating workloads seamlessly without altering the application code or investing in new hardware. It’s ideal for moving servers from on-premises platforms like Kubernetes or VMware to cloud equivalents (e.g., GKE or EKS). Relocating is efficient, minimizes downtime, and is suitable for applications operating on VMware servers and local Kubernetes distributions.
Repurchasing
On-premise applications are replaced with cloud-native software (like moving to Salesforce for CRM or Workday for HRM). It often involves a licensing change and is suitable for businesses wanting cloud-native features without building systems anew.
Refactoring
This involves redesigning and rebuilding applications for the cloud. It’s a more intensive and costly approach but offers future compatibility and scalability. Suitable for complex applications needing performance improvement or compliance updates.
Replatforming
Replatforming is a variation of the rehosting strategy, often described as ‘lift, tinker, and shift.’ It involves making minor configurational adjustments to applications to optimize them for the cloud without altering their fundamental architecture. This approach is used to modify how applications interact with databases, enabling them to run on managed platforms such as Google CloudSQL or Amazon RDS.
However, it’s essential to regularly review the progress of the re-platforming project to ensure it doesn’t inadvertently evolve into complete refactoring. The goal is to make only necessary changes and avoid extensive modifications that could increase complexity and cost.
Replatforming is particularly suited for organizations that are cautious about cloud migration. It allows them to gradually build confidence in cloud solutions while still reaping benefits like enhanced system performance and cloud-specific optimizations. This approach balances minimal disruption and leveraging some of the cloud’s advantages.
It is ideal for organizations contemplating a transition to the cloud yet cautious about the risks associated with migrating legacy applications all at once.
Retiring
This approach involves decommissioning obsolete or unused applications, thereby reducing maintenance costs and focusing the migration on essential applications. It’s best for organizations with redundant or outdated workloads.
Retaining
Suitable for applications that can’t be retired and need to remain in their current environment. This is often chosen when an application depends on another yet-to-be-migrated system or when there’s no immediate benefit in cloud migration. It’s also applicable for workloads that must run on local data centers for compliance or security reasons.
Benefits of transitioning to the cloud
Adopting cloud technology without a well-thought-out strategy can result in significant issues like data loss, increased downtime, budget overruns, and missed deadlines.
In contrast, implementing a strategic framework for cloud adoption identifies the most efficient, cost-effective, and least disruptive route from old systems to a cloud-based setup, addressing potential challenges and ensuring successful migration.
Here are the key advantages of strategic cloud migration:
Enhanced digital experience
Cloud services are accessible from anywhere, improving employee and customer experiences. This aids in digital transformation, enhancing customer interactions and equipping staff with modern tools. A strategic approach can automate the migration, ensuring continuous operation with minimal interruption.
Cost efficiency
A carefully planned migration strategy can significantly reduce costs by optimizing cloud resource use and avoiding unnecessary expenses like licensing and maintenance fees.
Enhanced security measures
Cloud providers offer better security features to protect sensitive data and comply with industry standards. Enhanced security tools and automated updates in cloud environments help mitigate security risks.
Data protection
Cloud infrastructure supports quick data recovery in emergencies, ensuring business continuity with minimal latency or data loss.
Improved performance
Cloud resources provide easy access to data from any location, reducing downtime and boosting system performance. Cloud applications for file sharing and workflows improve team collaboration, facilitating real-time updates and efficient project management.
Streamlined communication
Cloud-based communication tools improve team interactions, speeding up project completion and customer service. Effective communication boosts the employee experience and teamwork.
Elasticity and scalability
Cloud platforms offer flexibility and scalability, allowing organizations to quickly adjust to changing resource needs. They can expand during peak times and scale down when demand is lower, providing unmatched agility to meet evolving business requirements.
Challenges associated with migrating to the cloud

Ensuring a smooth application migration is a crucial challenge for modern organizations. Even with the right cloud provider, the migration process entails various risks. Key issues to consider during the transition to the cloud include:
Cost management
Overspending is a risk without a thorough understanding of the costs involved in cloud migration. This includes development, cloud hosting, hardware and software changes, and labor costs. Using cloud monitoring tools to track resource and application usage helps optimize cloud expenses.
Finding yourself stuck with a particular vendor
This issue arises when cloud services are not transferable to other platforms, making it costly and time-consuming to switch providers. Organizations often find themselves stuck with a provider that may not meet their evolving needs.
Security and compliance issues
Cloud migration introduces new security challenges. Collaborating with major cloud providers and cybersecurity experts is crucial for planning a secure migration strategy. This strategy should encompass data encryption, vulnerability scanning, access control, a cybersecurity mesh, and adherence to relevant regulations.
Lack of defined strategy
A haphazard approach to cloud migration can lead to failure. Successful cloud adoption necessitates a comprehensive, end-to-end migration plan, considering each application and dataset’s unique requirements and migration approaches.
Resource management and training
Cloud migration often requires new IT management roles. Internal IT teams may need more skills, particularly in industries with stringent data security compliance standards. Adequate training for IT staff is essential to bridge this skill gap.
Downtime
Network disruptions are a significant risk when transferring large data volumes to the cloud. A solution is maintaining a backup IT environment to run applications during migration. However, these temporary servers may not withstand high user loads, so managing user workloads and communicating potential capacity limitations and intermittent outages to users is essential.
Step-by-step-guide for a successful cloud migration strategy
Your cloud migration process will vary depending on your business type and company size.
Regardless of the chosen method, your cloud migration strategy should encompass these essential steps:
Evaluate your readiness for the cloud
Begin with a readiness assessment to ensure all aspects are considered. Review your current environment, including corporate and remote workforces, business needs, and priorities.
Assess your data, regulatory and security concerns, existing infrastructure, applications, and dependencies. Define your migration and modernization objectives, documenting desired outcomes and motivations such as cost savings or increased agility.
Next, determine what will be migrated, considering data and analytics workloads, networking latency, data volumes, and licensing stipulations. Form a cross-functional team including IT, finance, and business owners to ensure a shared understanding of the migration’s impact and expected results.
Assess your readiness to tackle technical debt and move away from legacy systems, considering if a cloud-native approach aligns with your goals.
Plan for your cloud migration move
Create a detailed migration plan after establishing business objectives and evaluating cloud readiness. This plan should outline the migration roadmap, workload migration sequence, preferred cloud architecture, and necessary application or data modifications.
Selecting a suitable cloud provider that matches your business objectives, financial constraints, and security needs is essential to prevent dependency on a single vendor. Evaluating aspects like cost-effectiveness, scalability, dependability, security features, and the provider’s future technology plans is vital.
Considering a multi-cloud strategy can help reduce the risks of depending on a single vendor, allowing you to take advantage of the unique strengths of various providers. You should also address compliance and security requirements related to the migration.
Following this, decide on the cloud migration strategy you choose, whether it’s seven types of client migration strategies that focus on the individual tool or workload implementation or an approach that considers an all-at-once, phased, or hybrid cloud migration approach.
Assess your environment to determine factors governing the migration, such as application data, legacy data, and application interoperability. Determine your data reliance and compliance requirements, and plan for data encryption at rest and in transit. Also, consider the underlying infrastructure, systems, and processes necessary for a successful cloud migration.
Organize a test before executing the actual migration plan
A testing plan ensures a smooth migration process and minimizes risks. Test migrations assess readiness and help identify potential issues before this strategic change. Detail KPIs to monitor the success of the migration, both technically and business-wise.
Regularly evaluate these KPIs to assess migration success and justify continued investment. Update and test your disaster recovery plan (DRP) to address potential downtimes during the migration. Training IT and app development teams in cloud technologies, migration tools, and operational processes is also vital to scale migration efforts efficiently and set your organization up for success.
Initiate cloud migration
After addressing any issues in the testing phase, the migration phase involves transferring data, applications, and other workloads to the cloud. It’s crucial to closely monitor migrations to ensure they progress as intended and resolve any emerging issues quickly.
Begin by setting up the foundational infrastructure, which includes choosing a cloud provider and establishing identity access management, network configurations, security protocols, tagging, cost management, and automation systems.
Automation is vital in streamlining the migration process, reducing errors, optimizing operations, minimizing downtime, and cutting costs. Employ middleware tools to automate tasks, set up continuous integration and delivery workflows, and adapt to changes in the cloud environment. Start migrating data by choosing a strategy: moving one database at a time, using a phased approach, or transferring all data simultaneously.
Then, proceed to migrate applications, ensuring proper configuration and that scheduled tasks function. Validate that each migrated component works in the new environment before proceeding with the next. Additionally, find a method to keep the source data synchronized during migration.
Validation may also encompass performance and load testing to evaluate the system’s scalability and responsiveness and user acceptance testing to ensure the end-user experience meets expectations.
Continue monitoring and optimizing cloud infrastructure
Post-migration, it’s vital to ensure the cloud environment is optimized and secure and that data is easily accessible. This stage involves managing cloud workloads, which includes monitoring performance, resource management, and upholding security and compliance standards. Organizations should continually use feedback and performance data to refine operations and enhance cloud efficiency.
Remember, cloud migration is an ongoing process rather than a one-time event. Your cloud migration strategy should include regular assessments for improvements in performance and efficiency. Continuous, real-time monitoring of infrastructure and data is critical to fully leveraging the cloud features and securing long-term migration success.
Be ready to update or upgrade software and security measures, adjust scaling based on demand fluctuations, and monitor cloud expenses to maximize cost-effectiveness and drive greater business value.
The next steps for using a cloud migration strategy to transform your business
Transitioning to the cloud can create opportunities for your digital workplace, enabling innovation, enhancing performance, improving user experiences, and realizing cost savings.
As you embark on migrating your digital assets to cloud infrastructure, you must have confidence in both the process and the expected results.
Despite several challenges in even the most successful cloud migration strategies, it’s essential to recognize that the journey to the cloud can be smoother with the proper knowledge and guidance.
Achieving a seamless cloud migration necessitates meticulous planning, thorough testing, and efficient allocation of resources, all of which serve as the compass guiding your strategy.


