When asking why customer service is important, the best way to start is by understanding exactly the value of customer service, both to the business and to the customer.
Businesses, after all, can be defined as goal-oriented processes, whose purpose usually focuses around profit and value creation.
Customer service, as we will discuss in this article, plays a vital role in value creation and affects business performance. It is important, therefore, to understand what it is and how to best deliver it.
Why is customer service important?
According to Salesforce, customer service refers to the “support you offer your customers – both before and after they buy and use your products and services – that helps them have an easy and enjoyable experience with you.”
For some, it may not always be easy to connect positive customer experiences to organizational performance. As a result, it may be difficult for some business leaders to justify expenditures on business functions that improve the customer experience.
There are several ways that customer service can positively impact business performance, however. A few of these include:
Better customer experiences translate into greater customer loyalty. Quite a few studies have shown that customer experiences directly affect customer retention. PwC, for instance, found that 32% of all customers would stop doing business with a brand they loved after just one bad experience. Similar results have been found by a number of other surveys and studies.

A better brand reputation. In one quote that has now become famous, Jeff Bezos said that if you “make customers unhappy in the physical world, they might each tell 6 friends. If you make customers unhappy on the Internet, they can each tell 6,000 friends.” In today’s world, the offline and online world have merged, so even brick-and-mortar businesses must understand how experiences affect their reputation.
Improved product adoption and engagement. Customer care often plays a greater role when customers are first adopting new products and services. During this stage of the customer journey, they must often learn new processes and procedures related both to the brand and the products. The more support they have, both in the short- and long-term, the more likely they will be to stay engaged with the product.
Ultimately, customer service should be considered a part of the product or service pipeline, since it directly affects customers’ ability to engage with, use, and gain value from their products.
Good vs bad customer service
Once the importance of customer service has been established, the next logical question is, “How do you deliver good customer service and experiences?”
There are different schools of thought on how companies should approach this question.
Warren Buffett, for instance, says that companies must not just satisfy their companies, they must delight them.
A number of professionals agree wholeheartedly and have built their entire customer service philosophy around such an approach. HubSpot, for instance, even recommends using a “customer delight index” metric to gauge how delighted customers are by your products and services.
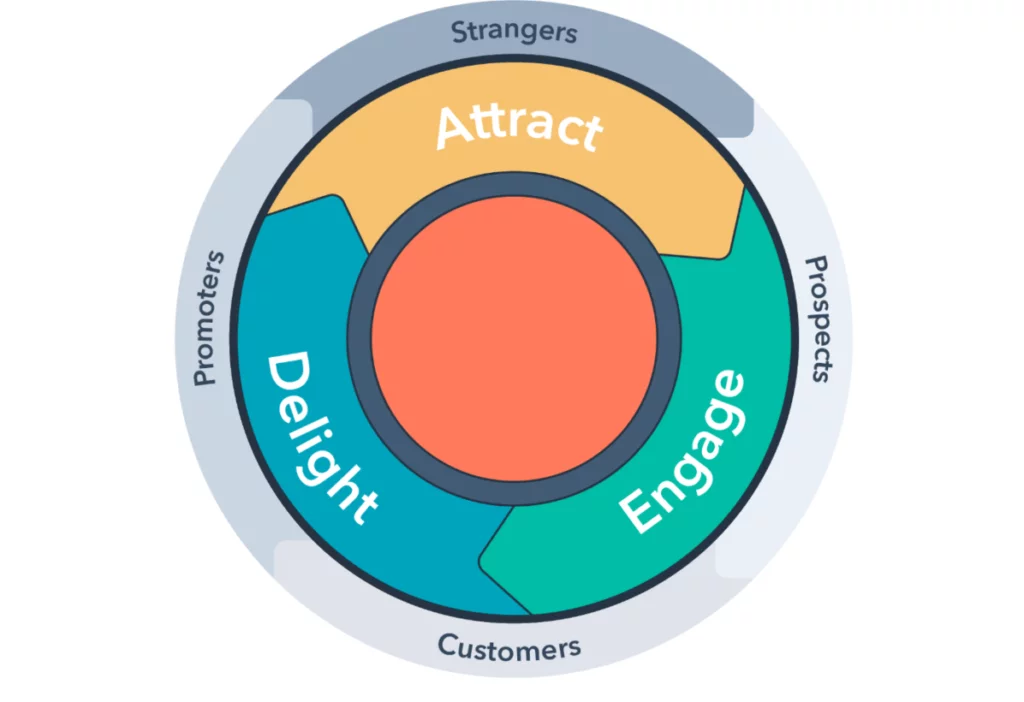
Others, however disagree.
One study published by the Harvard Business Review went in-depth to uncover how customer service affected loyalty and which activities raised loyalty, among other things.
Among their most critical findings: delighting customers doesn’t build loyalty, but reducing customer effort does.
When reviewing such contrasting viewpoints, it is worthwhile to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to this question.
Instead, it is important to remember that a wide range of other factors come into play, such as the expectations of a specific customer base, the product or service in question, and the company’s culture.
Rather than encoding a customer service philosophy from the outset, businesses should understand their own customers’ needs, then use their input to ensure that their customer service department can deliver on those expectations.
The impact of the employee experience on customer service
Customer service is a strong component of the customer experience. What may be less evident, however, is the role that the employee experience plays in customer service.
The employee experience – the sum total of interactions an employee has with their employer – affects countless areas of a business, customer service included.
Work environment, organizational culture, management, and other aspects of the employee experience have a direct impact on employee metrics such as:
- Productivity
- Performance
- Job satisfaction
When employees have the right work environment, skills, and tools, they will be far more prepared and motivated to deliver good customer service.
For example, one of the best ways to directly affect both employee productivity and customer service is by providing employees with modern software, such as CRM tools or tools that enable self-service, such as digital adoption platforms (DAPs).
Measuring and improving customer service: best practices
One of the best ways to ensure that customer service practices are delivering on their results is by taking a goal-oriented, data-driven approach.
Namely customer service professionals should:
- Set goals tied to organizational performance, customer satisfaction, and other important metrics
- Create customer service strategies and plans to achieve those goals
- Develop a set of KPIs that can be used to understand the health and ROI of the customer service program
- Continually collect customer data and feedback, then use that input to enhance customer care over time
A data-driven approach is advantageous for several reasons:
Companies can create benchmarks that are most useful to them. Data-driven approaches keep businesses focused on immediate customer needs, not abstract customer service philosophies. Those philosophies may be useful, but to generate real value from a customer service program, it is important to stay focused on real-world data and customer needs.
Customer service specialists can design experiences that are more relevant to their customer base. Every audience will have different needs and expectations. Those needs will depend on a number of factors, such as the brand, customer demographics, and the industry. By taking these types of considerations into account, customer service professionals will be able to deliver experiences that are more relevant and useful to their audience.
Data-driven and customer-driven approaches are more agile and relevant. The economy and customer needs change constantly. To stay relevant, therefore, companies must be prepared to change as well. Using data and customer input to drive customer experience decisions will enable organizations to become more agile and adaptable – and, as a result, deliver experiences that are more relevant and useful to their customers.
An approach such as the one covered here can, in short, help companies maximize the value of their customer service programs, even when customer needs and expectations evolve.
The current state of customer service
Customer expectations continually change, and there are countless factors that contribute to those evolving needs. Time, culture, the state of the economy, and technological advancements represent just a few.
Today, for instance, digital technology has become a major influence on the state of customer service.
Here are a just a few examples of trends that are currently influencing customer expectations:
Online customer service. To keep up with today’s digital consumer, online customer service is no longer an option, it is a necessity. In many cases, this means being able to communicate with customers through their preferred channels, whether those channels are email, social media, or telephone. However, with the right back-end technology, businesses can both reduce complexity while also improving the customer experience.
Automation and self-service. Automation is one way to reduce complexity and overload for employees, while also streamlining the customer service process. Chatbots, virtual assistants, and self-service web portals, for example, can help customers find answers to questions more quickly and efficiently – oftentimes without the need for human intervention.
Contactless payments. Contactless payment options, such as digital wallets, have been available for some time now. Yet with the arrival of COVID-19, they are becoming more prevalent. And in some cases, they are the preferred choice. In the post-COVID era, or the next normal, as McKinsey calls it, businesses should be ready to accommodate customers who prefer these payment options.
Since trends such as these are becoming predominant, customer service specialists should connect with their own customer base and be ready to adapt their customer experiences as needed.


