Alternative organizational structures challenge the concept of a traditional hierarchy, offering greater business agility and employee engagement. These flatter, more flexible structures empower employees and can lead to faster decision-making and a more responsive organization.
One emerging alternative is the holacratic organizational structure. This structure dismantles the rigid pyramid of a traditional hierarchy. Instead, authority and decision-making are distributed across self-organizing teams. These teams are empowered to operate autonomously, fostering a sense of ownership and improving the employee experience.
In this article, we’ll explore the key elements of holacracy, diving deep into its core principles and practices. We’ll look at the best practices for implementing holacracy in your organization, ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing its benefits. We’ll also discuss the potential challenges associated with this structure and how to navigate them effectively.
Lastly, we’ll provide a real-world example of a company that has successfully implemented holacracy, highlighting its stark differences from traditional hierarchical structures.
What is a holacratic organizational structure?
The holacratic organizational structure distributes leadership responsibilities among all team members. This approach contrasts with traditional corporate structures, concentrating power in a hierarchy. Individual team members gain more agency and can work on projects that align with the organization’s goals.
Brian Robertson developed the concept and dynamics of holacracy. He did this while running Ternary Software, a software development company. In 2007, he and Tom Thomison founded HolacracyOne. They published the Holacracy Constitution three years later.
What are the key elements of a holacratic organizational structure?
The key features of a holacratic organizational structure are:
Dispersed management system
Holacracy features a dispersed management system. It allows every team member to contribute to decision-making. Unlike traditional leadership groups, holacracy fosters a fluid management style. This approach instills a sense of purpose and promotes teamwork throughout the organization.
Roles instead of job descriptions
In holacracy, roles replace traditional job descriptions. Each role includes a purpose and its own responsibilities. You can create roles based on the business’s needs. When a role is no longer needed, the person transitions to a new role. Individuals hold many roles in various teams.
Responsiveness and flexibility
Roles make an organization responsive to business needs. Unlike rigid traditional structures, holacracy bases actions on achieving desired results. The key role, the Lead Link, assigns roles and allocates required resources.
Different governance process
Holacracy’s unique governance process empowers employees. They can propose changes to the organization’s processes, which the entire team evaluates and approves. Instead of fixed-job responsibilities, individuals in a holacracy occupy several roles. Each role has a specific purpose, domains, and accountabilities. For example, a CEO might lead one team while holding a subordinate role in another.
Integrative decision-making
Holacracy uses integrative decision-making. This system focuses on gathering relevant input. It also helps make decisions that suit the organization. It differs from consensus-based or consent-based systems. Holacracy outlines processes for organizing teams to fulfill a company’s operational needs. Each employee completes specific duties for effective teamwork.
Role fluidity and self-organization
In a holacratic organizational structure, roles change when combined or split. Every unique purpose or organization must have at least one circle. This is regardless of its size. Employees do not have assigned positions or job titles.
They work on projects that interest them and support organizational goals. This role fluidity allows team members to benefit from job rotation and apply their skills across different departments.
Circles are the major units of a holacratic structure. Each circle comprises individuals sharing responsibilities within a company. There can be an unlimited number of circles. Some circles can exist within larger ones. Circles must align with the company’s purpose and contain different roles.
Agility
Holacratic organizations are more agile, adaptable, and efficient. With less hierarchy, they aim to reduce bureaucracy while fostering innovation. This new business structure allows companies to operate at peak capacity.
What is the difference between a holacratic and a traditional hierarchical organizational structure?
A holacratic system often replaces hierarchical organizational structures. It establishes a flat workplace where team members wield equal influence under authority.
Here are the major differences between the two:
| Holacratic | Hierarchial | |
| Decision-making | Employees can make decisions about their roles. | Those higher up have the main say. |
| Roles | Each employee has multiple roles at a time. | Each employee has one role. |
| Type of system | Decentralized | Centralized |
| Type of collaboration | Cross-functional | None. Employees tend to work in siloes. |
| Type of company it is suitable for | Those used to rapid change. Also beneficial for smaller companies. | Beneficial for larger companies |
What is an example of a holacratic organizational structure?
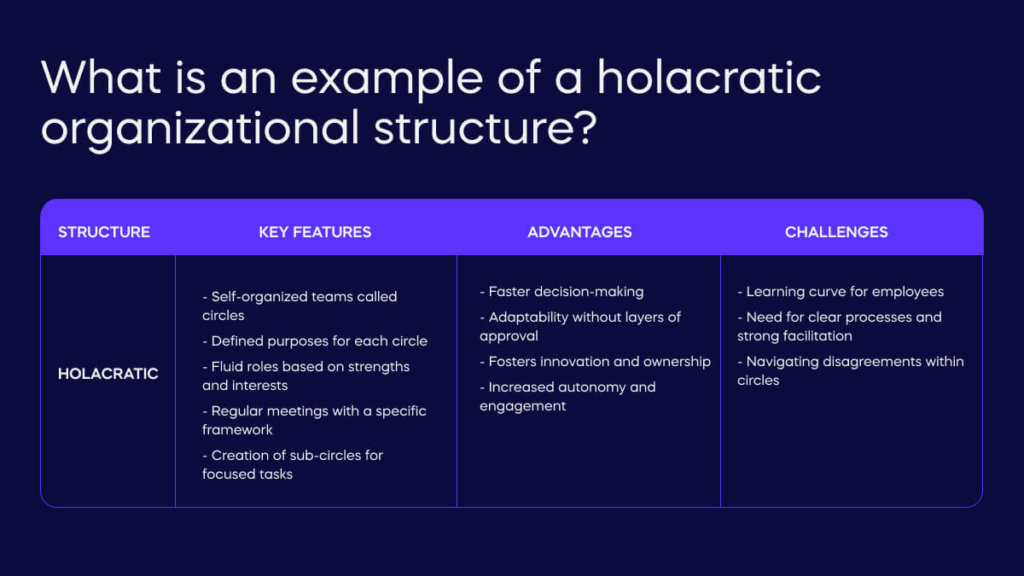
Buffer, the social media management platform, embraces a holacratic organizational structure.
This approach ditches traditional management pyramids. Instead, Buffer empowers self-organized teams called circles. Each circle has a clearly defined purpose, like building a new feature or managing customer support. Roles within the circle are fluid, with members taking on responsibilities based on their strengths and interests.
Regular meetings using a specific framework ensure clear communication and shared decision-making. The circle can even create sub-circles for focused tasks or dissolve roles that are no longer relevant.
This structure offers Buffer advantages like faster decision-making as teams can adapt to changing needs without layers of approval. It fosters innovation as employees feel ownership and contribute fresh ideas.
Additionally, increased autonomy leads to higher engagement among team members. However, holacracy also presents challenges. There’s a learning curve as employees adjust to this new way of working. Clear processes and strong facilitation are crucial to navigating disagreements within circles.
Best practice for implementing a holacratic organizational structure

Here are the best tips to help you put a holacratic organizational structure in place:
Cultivate a positive attitude
Embracing holacracy requires an open-minded approach from company leadership. Leaders must commit to giving holacracy a fair chance and reinforce the reasons behind the company’s interest in this organizational structure.
Have realistic expectations
Setting realistic assumptions and goals when transitioning to holacracy is paramount. It relies on the trustworthiness of team members. A holacratic structure won’t fix issues with problematic employees. A successful change management plan requires the skills and mindset of all employees.
Define the vision
Defining a clear vision is paramount when implementing a holacratic organizational structure. This vision aligns every stakeholder toward common goals and ensures that all employees are working towards the same goal with clarity and purpose.
Form circles and assign roles
Break down the business’s work into clear sections. This is the first step in forming circles. Defining roles within each circle ensures alignment with the organization’s objectives. The next step is assigning roles based on current job functions and skills. It’s imperative to remember that roles in a holacratic structure are adaptable.
Organize training and workshops
Familiarize everyone with the intricacies of the holacratic structure through employee training. These sessions will explain the roles and decision-making processes within it.
Discussing employee concerns and preparing them for the shift is critical. Clear communication during this transition phase is vital for its success.
Put in place new technologies
Introducing new technologies helps communication and collaboration when transitioning to holacracy. Collaborating with IT teams to identify and implement the right tools is essential. Leveraging tools to capture information about each role facilitates a smooth transition.
Test and refine the structure
It is advisable to test and refine the new structure before full implementation. Identifying key performance indicators helps gauge the transition’s effectiveness. Conduct regular check-ins to assess what’s working and what isn’t, allowing you to make adjustments in real-time.
Track and adapt as you go along
Monitoring the effectiveness of the holacratic structure is crucial for its long-term success. Identifying metrics to measure success and analyzing them provides valuable insights. Being prepared to refine roles and processes is essential for ongoing improvement.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement
Providing resources for skills gaps is vital for a culture of continuous improvement. Creating an environment that values learning from failures is also essential. Embracing an iterative approach contributes to organizational growth and success.
What are the benefits of a holacratic organizational structure?

The most important benefits of a holacratic organizational structure are:
Employee engagement
Involving all team members in decision-making promotes stronger employee engagement. As a result, employees feel more committed to its growth and development. Holacracy encourages small daily changes, responding to a changing environment.
This approach allows people within circles to make immediate improvements as problems arise, enhancing flexibility compared to traditional management.
Agile decision-making
Holacracy distributes decision-making authority across various roles, enabling quicker and more agile decisions. A decentralized approach allows organizations to respond faster to changing market conditions.
A holacratic structure also encourages individuals and groups to work towards their objectives. Aligning individual, team, and company purposes fosters a collaborative environment. This drives productivity and implements strategies that benefit business goals.
Cross-functional collaboration
Holacracy breaks down silos. It promotes cross-functional collaboration. It also encourages the exchange of ideas across teams and departments.
This collective intelligence harnesses the diverse skills and creativity within the workforce. It leads to innovative and effective solutions. Everyone in a circle knows their role and takes ownership.
They also understand their responsibility for solving structural problems. With role-driven decision-making, you can distribute power and authority. This ensures timely and well-informed outcomes.
Flexibility and adaptability
The holacratic structure provides adaptability to changing organizational needs. This system encourages small, incremental changes within teams to improve functionality.
Team members and circles can recommend procedural changes or improvements as challenges arise. This allows businesses to respond to delays with implementable adjustments.
Focus on results
A classical hierarchical system requires employees to present their work results to higher-ups. This can create unnecessary stress and misdirected effort. In contrast, a holacratic system shifts the focus from presentation to actual results.
This reduces tension and allows people to concentrate their energy on productive activities. Holacracy’s emphasis on autonomy and incremental change fosters a positive work environment. It builds a sense of community among self-managed teams.
Empowerment and transparency
Holacracy empowers employees to make decisions related to their expertise. This empowerment cultivates a culture of innovation and encourages initiative. The integrative decision-making process fosters transparency.
There are clear expectations without the barriers of higher management. Holacratic organizations can share operational updates, performance metrics, and organizational values, avoiding the bureaucratic hurdles common in traditional corporations.
Teamwork and community
The decentralized management of holacracy highlights the importance of communication and cooperation. Effective teamwork becomes essential for achieving results. This creates a strong sense of community. Self-managed teams can maintain a positive and healthy work environment.
This focus on roles allows for more flexibility in job assignments. The business can experience continuous improvement and adaptability by encouraging small, incremental changes.
Innovation and the encouragement to find solutions
Holacracy’s structure encourages teams to become more solution-oriented. Everyone within a circle understands their role. They take responsibility for finding solutions to structural problems. The people closest to the issues make the last calls. This leads to timely and well-informed outcomes.
This system empowers employees to make decisions in their areas of expertise. This fosters a culture of innovation and initiative. Holacracy reduces the traditional hierarchical pressures of presenting work to higher-ups. It allows employees to focus on producing actual results. It also directs their energy towards productive efforts.
It also facilitates sharing operational updates and employee performance metrics. Decentralized management in holacracy emphasizes the crucial role of communication and cooperation. These are essential for achieving strong team results.
What are the challenges of a holacratic organizational structure?

Like all organizational structures, the holacratic model also has its disadvantages.
They are:
Unneccessary tactical meetings
Tactical meetings play a crucial role in holacracy. Each circle conducts routine meetings to update on new ideas and project timelines. These meetings ensure everyone stays informed and aligned. However, employees often work within many circles, leading to several meetings. This overload can distract team members from important initiatives and reduce productivity.
Challenges of several roles
Holacracy requires individuals to take on many roles within different circles. This enhances flexibility but complicates fair compensation. For example, someone might develop software, plan events, and lead a circle.
Assessing pay becomes difficult because of the varied skills and time commitments involved. A holacratic structure requires a different mindset. It focuses on roles rather than job titles, and this new approach involves a learning curve.
Mindset change
Adopting holacracy requires a significant mindset change for employees and leaders. Traditional hierarchies provide clear guidelines and authority, while holacracy relies on distributed decision-making and self-management. Organizations can ease this transition by providing comprehensive training. These sessions teach employees to adopt a collaborative approach, helping them understand holacracy’s principles and navigate the new structure.
Slower decisions
Decentralized decision-making offers benefits but can slow the process. Some decisions need feedback from other roles or circles. Effective communication is essential. Regular meetings with leaders from different circles can ease alignment. These cross-circle meetings address issues and ensure smooth workflows.
Self-Governance
Self-governance has both advantages and disadvantages. Self-management empowers team members with creative opportunities. However, it can overwhelm employees who are used to senior managers’ guidance. Many roles may overload responsibilities, and context switching can reduce productivity. Leaders should track workloads and balance roles to prevent employee burnout.
Role ambiguity
Holacracy replaces job titles with roles and circles. This provides flexibility in assignments and quick adaptation to changes. But it can cause confusion and role ambiguity. Without clear responsibilities, work overlaps and inefficiencies occur. Transparency in role definitions and regular updates can prevent this. Adequate training helps clarify expectations.
Lack of accountability
Without higher management, holding team members accountable is challenging. Employee mobility complicates performance measurement. Transparent communication and clear role definitions are crucial. Establishing metrics and feedback mechanisms ensures accurate performance evaluation. Regular check-ins and reviews maintain accountability.
Key takeaways of a holacratic organizational structure
A holacratic organizational structure introduces a dynamic and flexible approach to organizational management.
Holacratic organizations can increase business agility and adaptability. These organizations can end bureaucracy with reduced hierarchy and politics while fostering innovation. This decentralized structure enables companies to operate at peak capacity with fewer people.
Holacracy allows businesses to respond to changing circumstances through procedural changes and improvements. This results-oriented approach reduces tension and directs efforts toward achieving tangible outcomes.
While it offers many advantages, it also presents challenges that need careful management. It requires focusing on effective communication and providing adequate training. It also requires digital adoption and maintaining clear role definitions.
Organizations should also focus on an incremental approach to holacracy. You must do this to minimize resistance to change. Embracing this new structure requires a shift in mindset. A holacratic organizational structure can lead to a more empowered and productive workforce.

FAQs
Holacracy decentralizes authority, enabling teams to make decisions within defined roles. This can accelerate operational decisions but may slow strategic alignment due to the need for consensus across multiple self-managed circles.
Enterprises with entrenched hierarchies may face resistance due to cultural inertia. Transitioning to holacracy requires significant mindset shifts, ongoing training, and adaptability, which can be challenging for organizations accustomed to top-down management.
Some organizations, like Medium, have reverted to traditional structures after finding holacracy impeded coordination on large-scale projects. Reintroducing hierarchy can restore clarity and efficiency in such cases.
Holacracy tends to be more effective in agile, growth-oriented environments where flexibility and rapid decision-making are prioritized over rigid structures.
By distributing authority and clarifying roles, holacracy can enhance employee engagement and accountability. However, it requires a culture that supports autonomy and continuous learning to be effective.

