You have the right digital tools, but do they bring in the highest revenue?
Optimization enhances operations, streamlines processes, minimizes resource utilization, and boosts performance, providing a cutting-edge advantage in today’s enterprise-driven landscape.
IT optimization propels organizations toward heightened efficiency and innovation in the digital transformation era.
Recent data from Statista reveal a projection that global IT spending is likely to reach an impressive $5.1 trillion by 2024, emphasizing the critical necessity of optimizing these expenditures for sustainable growth.
This article will explore essential aspects of IT optimization, covering its definition, benefits, challenges, comprehensive strategy, and practical examples.
What is IT optimization?
IT Optimization is the strategic refinement of business processes to boost efficiency and effectiveness. By fine-tuning operations, streamlining processes, and minimizing resource use, businesses can gain a competitive edge, capitalizing on strengths and adapting to market changes.
Companies can execute IT optimization at any point. Still, the typical time is when businesses undergo restructuring, such as mergers and acquisitions, evaluate assets, and optimize IT functions.
Your complete IT optimization strategy

A robust strategy is indispensable for the success of any IT optimization initiative. The aim is to ensure the process is a one-time endeavor, and often, the best way to achieve this is to establish Lean frameworks.
These systematic approaches, such as Kanban, Lean Six Sigma, and Scrum, prioritize efficiency by eliminating waste, improving processes, and fostering continuous improvement.
Implementing a Lean framework is a commitment that spans over six months. Once you have established your IT strategy, you can initiate optimization with well-defined targets and the appropriate tools to achieve IT optimization.
1. Specify the outcome and timeline
Before engaging in hands-on work, IT architects and strategists must delineate the desired outcome and project timeline for technology optimization.
This step involves collaborating with the relevant stakeholders to formulate a comprehensive plan.
This plan outlines the time and resources required to achieve successful IT optimization. During this phase, you identify your organization’s needs, encompassing processes, software upgrades, new technologies, and cloud migrations.
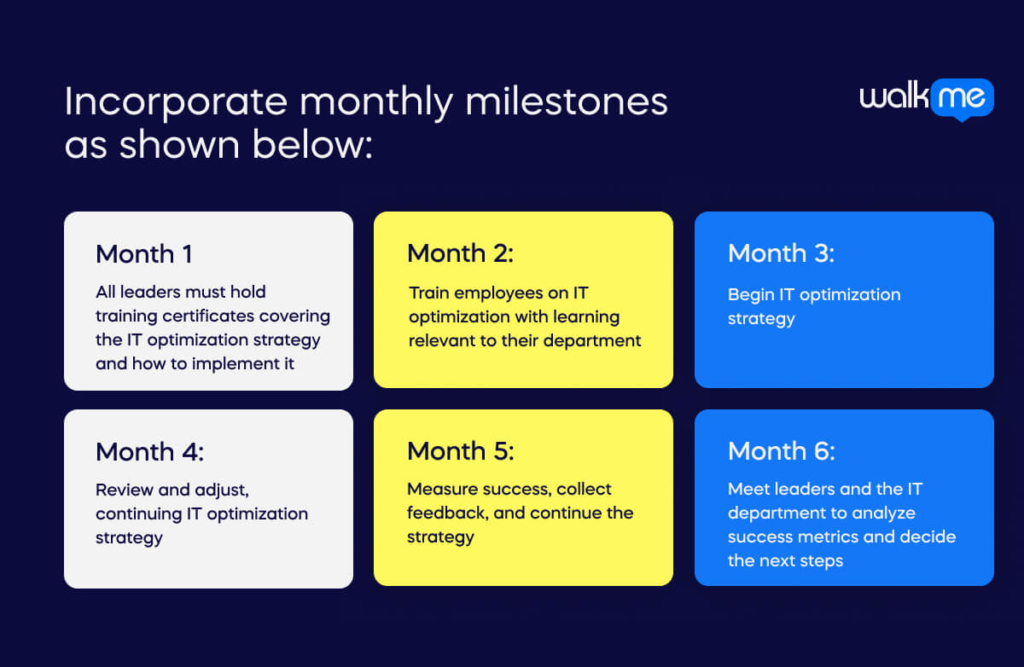
Incorporate monthly milestones as shown below:
- Month 1: All leaders must hold training certificates covering the IT optimization strategy and how to implement it.
- Month 2: Train employees on IT optimization with learning relevant to their department.
- Month 3: Begin IT optimization strategy.
- Month 4: Review and adjust, continuing IT optimization strategy.
- Month 5: Measure success, collect feedback, and continue the strategy.
- Month 6: Meet leaders and the IT department to analyze success metrics and decide the next steps.
2. Evaluate your current IT status
Assessing the present IT state is a pivotal aspect of IT optimization. IT assessments aim to identify gaps in current technology and highlight potential risks. Conduct comprehensive evaluations across all facets of the IT landscape.
Infrastructure
Every piece of hardware has a lifespan. Maintaining a checklist of company infrastructures, such as servers, networks, and storage, facilitates evaluating their value.
End-user computing
End-user computing includes printers, laptops, desktops, and smartphones. Given the rapid evolution of technology, many of these assets can quickly age or become obsolete/low-value.
Applications
The inventory of applications, especially Software as a Service (SaaS), has become integral to IT but can strain resources if not managed and accounted for effectively.
SaaS services are often procured without approval and remain unknown to the broader company. SaaS management platforms can help identify so-called shadow IT.
3. Chart business capabilities
Once you have established the IT state, the next phase involves mapping technology to business capabilities or processes.
The objective is to uncover gaps and redundancies, enhance value flow, and spotlight inefficiencies within business units.
Templates for Business Capability Maps
Business capability maps offer IT experts a synopsis of their business and technology architecture. Through these maps, you can make informed decisions on optimizing business units to align with the envisioned future IT state.
4. Optimize
Subsequently, organizations should optimize their technology.
The optimization stage involves standardizing technology interfaces and portfolios, leading to system consolidation and the creation of a leaner, more cost-effective IT infrastructure.
The primary areas for implementing IT optimization include applications, hardware, services, and IT projects.
Optimize unused applications
By streamlining and rationalizing applications, organizations can enhance efficiency, reduce complexity, lower the total cost of ownership (TCO) of their application portfolio, and decrease software spending.
Application optimization using robust portfolio management practices is a process that identifies redundant, non-compliant, and shadow IT applications, laying the groundwork for further cost-saving initiatives.
Eliminate Unused IT Hardware
Removing unused or outdated hardware helps businesses avoid annual server fees and storage expenses.
IT hardware elimination is a straightforward method to cut costs and allocate time for researching and implementing more cutting-edge and helpful technology.
End-user hardware in workplaces, such as desktop computers, printers, landlines, servers, and data storage, can all be upgraded, eliminated, or optimized.
Removing irrelevant IT hardware, like a fax machine, frees up space for new systems with higher business value.
Eliminate or scale back services.
Large companies often rely on outsourcing, and shared services can be a quick way to reduce costs. Access all service level agreements (SLA) to determine which IT services can be scaled back or temporarily eliminated.
Services include help desks, call centers, maintenance services, or contract workers.
SLA optimization involves auditing licenses, utilizing cloud computing services with built-in cost optimization tools, and shutting down or reducing usage instances on weekends, holidays, etc.
Optimize IT projects
Eliminating, removing, or adjusting projects can save organizations significant resources. A business capability map aids in discovering which projects can be prioritized or postponed based on their proposed value. Categorizing each project includes:
- High business value projects directly supporting the IT strategy.
- Increased business value projects do not directly comply with the IT strategy and require modification.
- Projects complying with the IT strategy but having little business value can lead to postponement.
- Abandon projects with low business value and no IT relevance.
5. Streamline
Efficiently optimizing a company’s enterprise architecture establishes a lean portfolio and enhances the organization’s overall business processes.
The application of three fundamental principles guides architecture optimization:
- Virtualization.
- Automation.
- Consolidation.
Virtualize
Making infrastructure more agile is a crucial aspect of IT optimization. Fine-tune infrastructure assets to meet current and future business growth. Examples of virtualization include:
- Eliminate redundant hardware by creating virtual desktop servers that operate on server pools accessible remotely.
- Enhance application services through grids that provide pools of application containers distributed across hardware servers.
- Improve business scalability at a lower cost by utilizing logical disk storage managers.
- Embrace Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) for automated IT system modernization.
Automate
Enterprise architecture and IT Asset Management (ITAM) facilitate the automation and modernization of all IT assets. Enterprise architecture aligns technology with business processes, creating solutions that align with business goals.
You can also use generative AI to optimize IT service via ChatBots, offering personalized responses and freeing customer support operators to focus on higher-level tasks.
Consolidate
Consolidating all data centers, applications, and systems is imperative for a robust IT infrastructure. Understanding the allocation of resources simplifies and enhances the process of improving systems, making it more effective.
6. Embrace Cloud Computing
By adopting cloud computing, businesses enable access to their platforms, services, and tools from any internet-connected device.
Cloud computing services encompass:
1. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
2. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
3. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Doing so eliminates the need for significant expenditures on technical equipment and the maintenance of large IT teams. You can also save or redirect the financial resources to other business areas.
7. Evaluate the Impact
A comprehensive review is essential to assess the success of the implemented technology optimization strategy. Consistently revisiting changes and monitoring IT costs and data allows for ongoing evaluation.
This process aids in determining the strategy’s effectiveness in targeted areas and identifies any areas that may require adjustments in the future.
If the optimization efforts prove successful, large-scale optimizations may not be necessary, as the IT infrastructure should now operate more efficiently than before.
What are some examples of successful IT optimization strategies?

Examples of successful IT optimization strategies show what optimization looks like in practice and how different approaches work in various industries.
Walmart
Walmart offers the first example of a successful IT optimization strategy.
Background
Walmart, a retail behemoth keenly attuned to market dynamics and the pivotal role of technology in business, recognized the imperative to reshape customer interactions with the brand.
With extensive resources, the company embarked on a journey of IT optimization, targeting customer-facing and back-office operations.
Objective
Drive innovation, combat competition, and digitize the shopping experience.
Approach
The challenge of integrating technology into business operations unfolded on dual fronts. Walmart sought to enhance customer services while overhauling internal management and administrative processes.
In 2018, Walmart committed over $11 billion to IT optimization significantly.
As part of its strategic expansion, the company forged partnerships with industry leaders, including Google for voice-enabled commerce and Microsoft for cloud computing.
Nike
The second example of IT optimization comes from the famous clothing manufacturer Nike.
Background
Nike, a prominent apparel manufacturer, prioritizes innovation and client comfort, aligning with their core mission and digital transformation strategy. The need for a robust online presence became evident when the pandemic hit, prompting the company to reassess and strengthen its e-commerce strategy.
Objective
Enhance the e-commerce strategy to establish online retail as a robust revenue channel.
Approach
In 2017, Nike boldly shifted away from wholesale, connecting with its clients directly. Despite 80% of profits originating from wholesale, Nike prioritized direct audience engagement to differentiate itself.
The brand developed an ecosystem to amplify the significance of Nike’s digital channels, exemplified by apps like Nike Run Club and Nike Training Club.
These apps offer training programs and foster a sense of community, transforming Nike into a lifestyle brand promoting health and excellence in sportswear.
Tesla
The following example comes from the innovative electric car manufacturer Tesla.
Background
From its inception, Tesla strategically leveraged technology to distinguish itself in the business landscape.
Positioned as a trailblazer, Tesla deviated from conventional industry norms, embracing transformative and innovative concepts.
The company offers its audience an array of impressive advantages—Tesla cars epitomize innovation, environmental consciousness, future readiness, and effortless maintenance.
The key to Tesla’s remarkable success lies in its adept use of IT optimization for its cutting-edge technology.
Objective
Utilize state-of-the-art technologies to redefine perceptions of cars and their functionalities.
Approach
Tesla is the sole global car manufacturer that implements software updates seamlessly over the air.
Setting itself apart, the company ensures clients effortlessly receive safety, performance, or convenience updates without manual intervention.
The manufacturer autonomously enhances the vehicle’s characteristics and capabilities, requiring clients only to download a software update through Wi-Fi and initiate the installation process.
What are the opportunities for IT optimization?
It is helpful to consider the best opportunities for IT optimization to minimize costs, such as those in the list below.
Applications
Applications encompass all in-house and third-party software the business employs for diverse functions. Rationalizing and modernizing these applications is crucial for IT cost savings.
Applications: Utilize IT optimization techniques by rationalizing and modernizing in-house and third-party software for cost savings and improved functionality.
Services
Services involve activities delivering IT services to the organization. Scaling down services during low usage optimizes resource allocation and enhances efficiency.
Services: Implement IT optimization strategies by dynamically scaling down services during periods of low usage, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing overall efficiency.
Infrastructure
Infrastructure, comprising servers, networks, and storage, represents the necessary hardware for business activities. Optimization involves upgrading and replacing old hardware with newer versions, ensuring improved performance.
Infrastructure: Apply IT optimization through regular upgrades and servers, networks, and storage replacements to ensure optimal hardware performance for business activities.
End-user computing
End-user computing involves all systems utilized by employees. These systems are identified and optimized through careful analysis or upgrades, enhancing overall efficiency and user experience.
End-user computing: Improve end-user computing experiences by incorporating IT optimization methods, ensuring efficient and seamless interactions with technology resources.
What are the benefits of IT optimization?

Numerous advantages come with IT optimization.
Strategic optimization and management of IT enable organizations to align with expanding business demands. This technological enhancement supports core business success, lowers costs, accelerates or automates processes, and enhances productivity.
IT optimization is crucial for organizations, irrespective of size or growth stage.
Here are the benefits:
Enhance profitability
By capitalizing on savings from IT optimization, businesses can reinvest in development and service improvements, gradually increasing company profitability.
Cost reduction
Following an analysis of the current IT landscape, assets can be upgraded, modified, or eliminated, effectively reducing unnecessary costs and providing long-term financial savings.
Simplify operations
Streamlining IT processes is a crucial advantage of optimization. This simplification results in faster-running applications, increased agility, and an enhanced user experience.
Automating business processes is an effective means of reducing complexity and freeing up valuable time.
Cut compliance and governance expenses
Aligning the company’s technology strategy with its business goals is vital. IT optimization facilitates contract negotiations and the removal of tools with limited value, thereby keeping governance costs at a minimum.
Enhance productivity and facilitate growth
IT optimization aims to boost productivity and foster growth over time. Automation of processes, simplification of internal operations, and overall cost reduction contribute significantly to achieving these goals.
What are the challenges of IT optimization?
Technology optimization faces various challenges, including a scarcity of resources, heavy workloads, the surge in remote work, and insufficient visibility across different IT domains.
Organizations may not recognize the significance of optimizing their IT infrastructure unless they operate on lean or agile principles to streamline processes.
Here are the challenges:
Scarcity of resources and time
A primary challenge in IT optimization is the limited availability of resources and time.
Successfully implementing an optimization strategy requires effort and time, yet it proves to be an investment in the overall growth and success of the business, fortifying its foundation.
Repetitive optimization
Organizations operating outside a lean or agile framework often use similar optimization efforts.
With a well-defined plan and targeted actions, comprehensive optimization becomes a periodic necessity, occurring only every few years.
Surge in remote work
The increasing prevalence of remote work poses challenges in streamlining business activities to improve productivity.
Employees working outside the office necessitate new technology, security measures, and efficient operation applications, prompting extensive optimization measures.
Analytics and data management
Organizations lacking transparency in business and IT domains encounter difficulties optimizing their systems.
Before defining a technology roadmap, a thorough IT assessment is essential to identify the current state before you attempt to improve efficiency.
Transform your IT landscape today for long-term sustainability
Businesses should proactively embrace optimization strategies for agility, cost-effectiveness, and responsiveness. The success of IT optimization depends on a multifaceted approach aligned with organizational goals. Specifying outcomes, collaborating with stakeholders, and adopting lean frameworks create an environment where IT fuels business growth.
Understanding the significance of well-defined targets, appropriate toolsets, and collaborative planning empowers organizations to extract maximum value from IT investments.
Our examples, from cloud cost management to virtualization, illustrate the approach’s versatility. Businesses can elevate their IT performance by integrating these strategies into overarching plans.
As technology evolves, proactive adoption of IT optimization strategies emerges not only as a best practice but as a business imperative. The journey toward IT optimization is a continuous refinement, adaptation, and innovation cycle, offering enterprises a resilient pathway to sustained success.


