Process automation uses technology and software solutions to design, execute, and control workflows and business processes independently from humans.
These solutions are designed to mimic human capabilities to complete repetitive organizational functions, especially when tasks are rule-based and well-defined.
The impacts of continuous technological developments are being felt industry-wide, expediting transformation efforts across various sectors.
In a world fueled by digital disruption, the benefits of developing technologies (Machine Learning and AI) have reimagined traditional approaches to process automation entirely.
Modern applications for process automation now utilize human-trained ML algorithms. These solutions aggregate, organize, and manage large amounts of proprietary data automatically by AI to detect patterns, anomalies, and trends in a given process more accurately.
This enhances decision-making capabilities and reduces human error by relying on a more mechanical methodology for completing tasks.
This article explores the fundamentals of process automation and its crucial role in contemporary businesses. It examines key benefits, impacting technologies, real-world examples, and implementation stages for a concise understanding.
What is process automation?
Process automation refers to the application of technology and software solutions that enable the creation, deployment, and supervision of workflows and business processes without direct human involvement.
These solutions emulate human capabilities, particularly in situations where tasks are rule-based and clearly defined, aiming to efficiently complete mundane and time-consuming business functions.
Process automation solutions have historically represented a specific segment within wider business process management (BPM) but have now become a key component for elevating operational standards and driving transformation efforts.
Research shows that 94% of companies undertake repetitive and time-consuming tasks. Automation has significantly enhanced the roles of 90% of knowledge workers, resulting in increased productivity for 66% of them.
Why is process automation important in business?
Deploying process automation has become a key prerequisite of modern business process management and is instrumental in facilitating transformations in today’s technologically disruptive arena.
In a Camunda survey, 97% of enterprise IT decision-makers recognize the critical role of process automation in digital transformation. Additionally, 84% of respondents intend to boost their investments in process automation.

- Operational efficiency: Automation enhances operational efficiency by reducing manual intervention and ensuring the consistent and precise execution of processes.
- Value creation: Businesses can discover new forms of value creation as process efficiencies are strengthened, allowing the reallocation of time previously spent on standardized tasks towards more critical objectives.
- AI and ML integration: Combining the power of AI and ML with workflow automation enables predictive capabilities, learning from Big Data, spotting trends, and improving decision-making during workflow implementation.
- Workflow automation independence: Workflow automation, a vital component of contemporary business process automation, is designed to run independently, ensuring tasks follow a defined workflow sequence.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) advancements: Businesses experience advances in RPA through AI and Big Data, with RPA systems being most effective when relying on numerical, quantitative data.
- Utilizing unstructured data: Large amounts of unstructured qualitative data sources, such as databases, photos, documents, and digital platforms, are often underutilized due to challenges in efficient processing.
- AI, ML, and NLP integration: AI, ML, and Natural Language Processing (NLP) can analyze large datasets, manage structured and unstructured data, and provide insights and feedback to RPA systems.
What are the benefits of process automation?
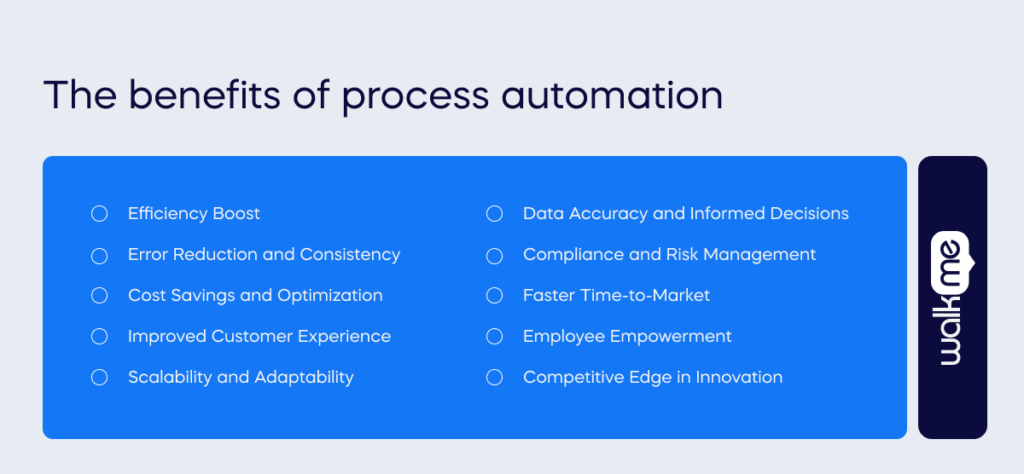
Deploying enhanced process automation solutions across various functions can deliver a range of benefits for businesses.
It can lead to gains in employee productivity, resource savings, and a downturn in error rates. For this reason, IT leaders should increase their strategic focus on enhancing automation capabilities to stay ahead.
In a PwC survey, 73% of respondents believe that technology can never replace the human mind, while 37% express concerns about automation threatening jobs.
Below, we explore the top benefits and reasons why enhancing process automation efforts should be firmly within the purview of CIOs, CDOs, and IT leaders aiming to achieve heightened operational efficiency:
- Efficiency Boost: Process automation accelerates tasks, boosting efficiency and allowing employees to focus on strategic aspects of their roles.
- Error Reduction and Consistency: Automated workflows minimize human errors, ensuring consistent and reliable outputs for an enhanced customer experience.
- Cost Savings and Optimization: Automation reduces operational costs, optimizes resource utilization, and mitigates the need for additional personnel.
- Improved Customer Experience: Automated processes enable quick responses and personalized services, enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
- Scalability and Adaptability: Automation scales seamlessly, accommodating increased workloads without proportional rises in operational complexities.
- Data Accuracy and Informed Decisions: Automated processes ensure data accuracy, empowering decision-makers with reliable insights for strategic decision-making.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Automation is crucial in ensuring regulatory compliance, reducing the risk of penalties and non-compliance.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Automation expedites critical processes, from product development to marketing campaigns, enabling a more agile response to market demands.
- Employee Empowerment: Liberating employees from mundane tasks fosters job satisfaction and empowers them to focus on tasks requiring creativity and strategic thinking.
- Competitive Edge in Innovation: Automation creates an environment conducive to innovation, providing a competitive edge for organizations exploring emerging technologies.
What technologies impact process automation?
In the years and decades ahead, automation and AI will likely fuel a profound shift in how we work and deliver value to customers.
Next Move Strategy Consulting foresees the AI market reaching almost two trillion U.S. dollars by 2030, up from its current value of nearly 100 billion U.S. dollars.
Below, we delve into some of the most prevalent technologies shaping the latest process automation solutions and explore their transformative impact on modern BPM.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is at the forefront of process automation. It involves the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. In the context of automation, AI is employed to analyze data, make decisions, and execute actions without direct human intervention. Machine learning, a subset of AI, enables systems to learn and improve their performance over time based on experience.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning empowers systems to learn from data patterns and experiences, evolving their functionality without explicit programming. In process automation, ML algorithms are pivotal in recognizing trends, predicting outcomes, and making informed decisions. ML is instrumental in optimizing processes, identifying anomalies, and adapting to dynamic business environments.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of AI that focuses on enabling machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language. In process automation, NLP is critical in bridging the gap between human communication and computer systems. It allows for automating tasks involving language comprehension, making interactions more intuitive and user-friendly.
Low-Code/No-Code (LCNC)
Low-Code/No-Code platforms have reimagined the way applications and processes are developed. These platforms empower users with varying technical expertise to create software solutions and automate workflows without extensive coding. LCNC accelerates the development lifecycle, fostering collaboration between business and IT and reducing the barrier to entry for automation initiatives.
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)
Intelligent Process Automation represents the convergence of traditional Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with cognitive technologies like AI and ML. IPA goes beyond rule-based automation by incorporating decision-making capabilities, pattern recognition, and adaptability. It enables organizations to automate complex, cognitive tasks, driving greater efficiency and accuracy in business processes.
Process automation examples
When looking at the potential of process automation, it may be easy to see specific applications in one’s own business. An organization with sufficient customer data could leverage that information to optimize product recommendations, personalize marketing experiences, and more.
Below, we explore prevalent application areas for AI and automation, such as risk modeling for predicting and assessing potential risks with pinpoint accuracy and compliance management, where AI utilizes sophisticated data analysis and pattern recognition to ensure organizations adhere to regulatory standards and requirements.
Regardless of the chosen solution, it is prudent to ensure that automation efforts align closely with the organization’s specific needs and overarching strategic goals.
Task Automation
In task automation, repetitive and time-consuming activities are streamlined through automated workflows. This can range from data entry and file organization to email responses, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and creative tasks.
Customer Service Management
Automation in customer service is revolutionizing how businesses interact with their clientele. Chatbots, automated ticketing systems, and self-service portals provide instant support, enhancing customer satisfaction while reducing the strain on support teams.
Customer Acquisition
Automation facilitates personalized marketing campaigns, lead scoring, and targeted outreach. Organizations can optimize their marketing strategies by automating customer acquisition processes, nurturing leads, and converting prospects into satisfied customers.
Product Recommendations
E-commerce platforms leverage automation to analyze customer behavior and preferences, delivering personalized product recommendations. This enhances the customer shopping experience and increases the likelihood of successful sales.
Risk Modeling
Risk modeling automation involves using advanced algorithms to analyze data and predict potential risks. This is particularly valuable in finance, insurance, and other industries where identifying and mitigating risks is crucial for success.
Invoicing
Automating the invoicing process ensures accuracy and timeliness in financial transactions. From generating invoices to tracking payments, automation reduces errors and accelerates the billing cycle.
Payroll
Payroll automation simplifies salary processing, tax calculations, and compliance tasks, streamlining payroll management. This saves time, minimizes the risk of errors, and allows businesses to allocate resources more efficiently and focus on strategic initiatives.
Employee Onboarding
Automated employee onboarding processes streamline the integration of new employees into the organization. This includes document submission, training modules, and setting up access to necessary systems, ensuring a smooth and consistent onboarding experience. Platforms with task automation capabilities, like WalkMe’s Digital Adoption Platform, can automate repetitive workplace tasks, freeing up employee time for more valuable activities.
Regulatory Compliance
Automation aids organizations in adhering to regulatory requirements by tracking changes in laws and automatically implementing necessary adjustments. This proactive approach reduces the risk of compliance-related issues.
Analytics-Driven Hiring and Retention
Organizations can automate hiring by utilizing data analytics, identifying top candidates, and predicting employee retention. This ensures a data-driven approach to talent management.
Recruitment
Automation in recruitment involves the use of applicant tracking systems, automated interview scheduling, and resume screening. This accelerates the hiring process and ensures that the best candidates are identified efficiently.
Logistics Network and Warehouse Optimization
Logistics and warehouse management automation improves inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and supply chain visibility. This results in cost savings and enhanced operational efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance
In industries relying on machinery and equipment, predictive maintenance utilizes automation to forecast potential equipment failures. By proactively addressing issues, organizations can minimize downtime and extend the lifespan of assets.
The stages of process automation
Several factors have spurred the ongoing race toward digital maturity.
A McKinsey survey shows that more than two-thirds of companies have accelerated their adoption of digitization and automation since the onset of COVID-19. Shifting consumer demands and supply chain disruptions continue to drive the transformation race.
This is evident in the recent surge in AI usage. According to a Statista survey, about 25% of companies saved between $50,000 and $70,000 using ChatGPT, while 11% reported saving over $100,000 since incorporating ChatGPT into their workflow.
AI and automation are already in wide use today. For a company that has yet to adopt these technologies, it may be difficult to integrate automation solutions into the business effectively and efficiently.
An organization’s evolving approach to business process automation can be determined through a progression of stages. Each stage brings its own set of challenges and opportunities that shape the organization’s capacity to adapt, innovate, and optimize its operations.
Below, we identify the key business process automation (BPA) stages so business leaders can ascertain the optimal progression for their organization’s automation journey.
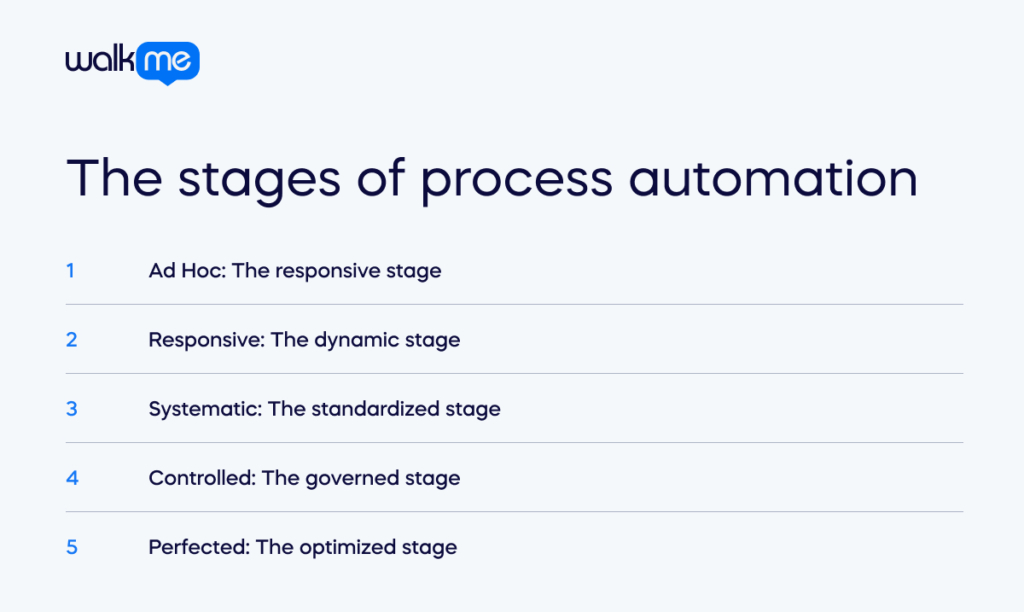
Ad Hoc: The responsive stage
In the Ad Hoc stage of business process automation, organizations address tasks case-by-case without a predefined or structured approach. Imagine an organization encountering a sudden surge in customer queries and choosing to automate responses to handle the immediate influx.
Ethos: Teams prioritize agility and responsiveness in this stage, crafting automation solutions as specific needs arise and adapting quickly to changing circumstances.
Responsive: The dynamic stage
The Responsive stage involves a flexible approach to automation, adjusting processes based on emerging opportunities or challenges. Consider an e-commerce company adapting its order processing system to swiftly accommodate a new product line.
Ethos: Teams here focus on being proactive, identifying opportunities and challenges, and responding promptly with automation solutions tailored to the evolving business landscape.
Systematic: The standardized stage
Moving into the Systematic stage, organizations establish standardized processes for automation. Picture a manufacturing company implementing automated quality control checks at predefined stages of production.
Ethos: Teams emphasize consistency and efficiency, developing standardized automation processes to streamline operations and reduce variability.
Controlled: The governed stage
Organizations take a strategic and governed approach to automation in the Controlled stage. Think of a financial institution implementing automated compliance checks, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements.
Ethos: Teams adopt a strategic mindset, focusing on governance, risk management, and compliance, ensuring that automation aligns with organizational objectives and industry regulations.
Perfected: The optimized stage
The Perfected stage represents a highly refined and optimized state of automation. Envision a logistics company using advanced predictive analytics to optimize supply chain processes seamlessly.
Ethos: Teams pursue continuous improvement, leveraging advanced technologies and analytics to optimize processes, enhance efficiency, and stay at the forefront of innovation in automation.
How will process automation reshape the future of business?
As business models and operating models evolve, so too will the workplace.
Task automation platforms, as mentioned, can deliver major productivity gains in the workplace. Employees will no longer need to spend time on repetitive, mundane tasks and can instead focus on more strategic initiatives.
Yet both employees and employers must understand how drastically automation could affect the workplace and the workforce.
According to McKinsey, increased global adoption of automation capabilities could impact over 800 million jobs by 2030. Automation and AI, in short, will reshape the workplace and redefine job roles, perhaps in ways that many of us can’t yet foresee.
In order to prepare for this inevitability and stay on the right side of change, most experts agree that proper employee training and lifelong learning should become foundational principles for employers and employees alike.


