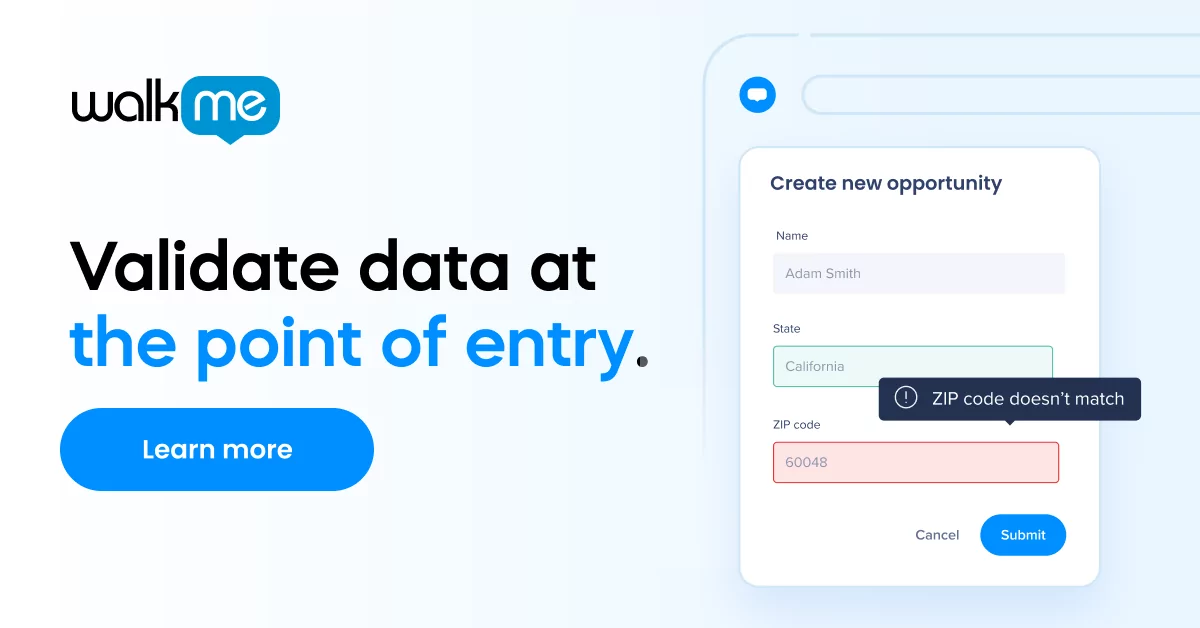
Understanding your customers in today’s economy can boost your sales team’s efficiency. Creating experiences that impress your customers fosters lasting relationships. These relationships, in turn, generate customer loyalty, consistent sales, and long-term business transformation.
By implementing a formal sales process, your sales team gains a clear framework. This makes it easier for the team to stay coordinated, track results, and integrate new members. Setting up or refining a sales process can propel your business to further growth.
This guide will cover what a sales process is and why it is important. Next, it will look at the typical stages of a sales process. We will discuss strategies for developing and enhancing your process and overcoming common challenges. Then, we will also look at what you will need for a sales process flowchart. Lastly, we will consider the metrics you need to consider for an effective sales process.
What is a sales process?
A sales process is a set of repeatable steps followed by a salesperson. This process aims to build a business relationship that culminates in a sale. Each time a rep engages in these consistent actions to make a sale, they adhere to a sales process.
A sales process serves as a guide for your sales team. It helps them navigate prospects through the sales cycle stages until they become customers. Additionally, the most effective sales processes include steps or stages. These outline how salespeople can maintain customer engagement.
High-performing sales teams adhere to an established process. Managers implement this by training and coaching sales reps. They use digital tools to enhance lead generation and track opportunities. These tools also help manage the pipeline and communicate with customers.
Why is developing a sales process important?

A structured sales process stands as the foundation for any thriving sales operation. It provides sales teams with a clear path to follow. Far from just a set of guidelines, this approach embodies a strategic framework. It’s crafted to boost efficiency, uphold consistency, and elevate results.
The importance of developing a structured sales process is as follows:
Enhances your understanding of prospects
A sales process highlights the importance of prospect research. This encourages your sales team to understand the needs of their prospects. It also outlines buyer personas and ideal customer profiles.
This guidance helps sales reps identify those most likely to convert. Simplifying the sales journey, this approach keeps efforts on track. It acts like a GPS from the initial contact to the signing of the contract.
Streamlines the buyer’s journey
It’s crucial to understand where buyers are in their purchasing process. The sales process clarifies the actions needed at each stage. This reduces the chances of deals slipping through. Precise tracking and analysis of each stage’s performance are possible. This enables the identification of bottlenecks and strategy refinement for continuous improvement.
Allows a focus on high-value activities
A formalized sales process concentrates efforts on the most revenue-generating activities. Without a process, pinpointing what works can be challenging. The structured sales cycle assists in onboarding employees by showing the goals. It illustrates how each step supports the next and highlights areas for improvement.
Improves sales performance insight
A standardized sales process provides insights into each salesperson’s performance throughout the sales cycle. This includes email metrics and conversion rates. This visibility helps identify top communicators and those needing more support. Representatives can thus pace the sales process to match prospects’ readiness, maintaining trust.
Eases coaching and skill development
Standardizing the sales process simplifies coaching for new sales reps. It shows them the necessary actions in various scenarios. This accelerates learning and alignment with the company’s selling style. It also helps identify skill gaps for targeted training. Structured approaches filter out low-potential leads, focusing on those most likely to purchase.
Enhances lead quality and sales forecasting
Refining the sales process improves the generation of high-quality leads. This shortens the sales cycle and focuses on promising prospects. It also offers a clearer view of sales progress for more accurate revenue forecasting. Continuous engagement keeps deals moving and maintains prospect interest.
Facilitates efficient navigation and collaboration
Defining stages in the sales journey helps professionals navigate the process. Each stage has a specific purpose and action set. Adopting a common sales language eases communication across departments. This reduces confusion and enhances support from various teams.
Ensures consistency and accurate forecasting
A repeatable sales process brings deal-winning consistency. This allows for dependable forecasts of sales closures from a given number of leads. Predictability helps sales managers set realistic quotas. Aligning sales efforts with business goals drives revenue growth and sales success.
What are the main steps of a sales process?
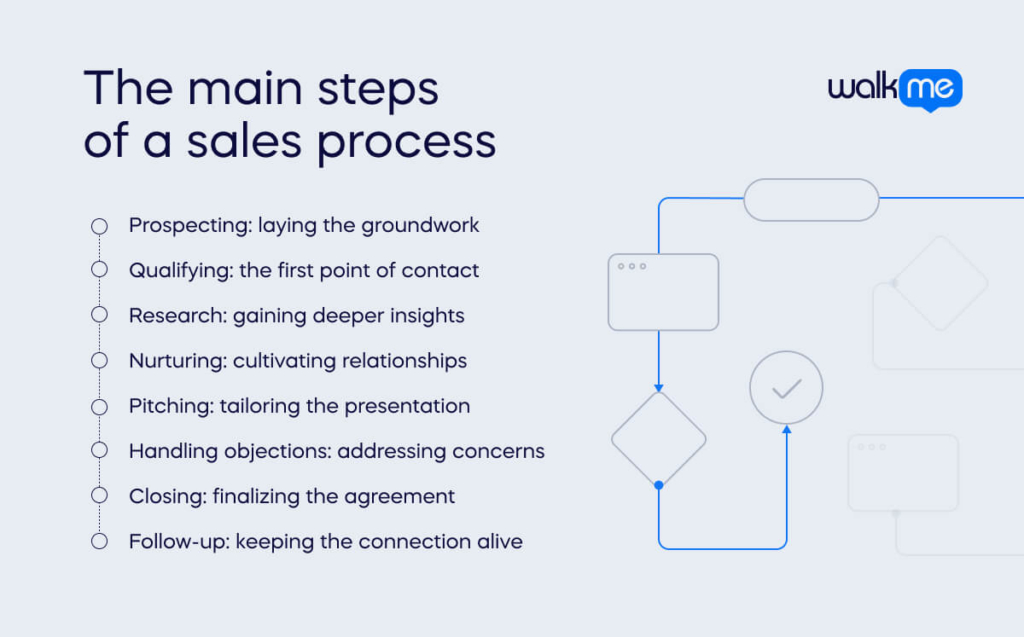
You can build a sales process on a sequence of stages, each marking a critical milestone in a sale. Within each stage, there are specific tasks. Your team must complete these tasks to move the sale forward from one stage to the next.
The steps in your sales process may vary. This variation depends on your industry and the detail level needed to secure leads.
Nonetheless, you need to plan strategies for every critical point in the sales funnel.
These are:
Prospecting: laying the groundwork
Prospecting is the first step in the sales process. It involves identifying new sales leads. This phase is fundamental because it sets the trajectory for all later stages. By prospecting effectively, sales representatives can focus on the most promising leads. This prevents wasting time on leads that may not progress further in the sales cycle.
Creating detailed buyer personas and customer profiles is vital to finding the right prospects. You can base it on the characteristics of past successful sales. Understanding the challenges these prospects face allows sales teams to position their offerings as solutions to these issues.
The prospecting toolbox is diverse, including both online and offline methods. Online strategies encompass email campaigns and social selling on platforms like LinkedIn. Offline methods cover cold calling and participating in conferences, webinars, and industry-specific gatherings. Generating leads through referrals from existing customers is another effective strategy.
Qualifying: the first point of contact
The qualifying stage involves the sales team’s initial direct interaction with a lead, usually a phone call or email. The aim is to collect enough information to see whether the lead fits your product or service.
The BANT framework is a helpful guideline at this stage. It evaluates a lead’s budget, authority, need, and timeline. This stage focuses more on building trust and gathering information than on selling.
Research: gaining deeper insights
Once you qualify for a lead, the next step is in-depth research. This stage involves a closer examination of the lead’s business. The aim is to thoroughly understand their specific needs and challenges.
Sales representatives look at available data such as company financials, websites, and profiles of company leadership.
Effective research allows you to frame offerings that address a prospect’s specific pain points. It recognizes that while many businesses in the same sector may share common challenges, each company is unique. Tailoring your approach based on detailed research is key to crafting a sales pitch.
Nurturing: cultivating relationships
Nurturing leads is about more than maintaining contact. It’s about building meaningful relationships. This stage involves educating prospects about your product, service, or the broader industry.
It also requires personalizing your communication to meet their specific needs. Forging a personal connection can make all the difference in today’s competitive market. It transforms prospects from simple contacts into loyal supporters.
Engaging with prospects through valuable content and support keeps your brand in their minds. It shows your commitment to being a helpful and knowledgeable resource in your field.
Pitching: tailoring the presentation
Understanding the prospect’s needs leads to the pitching stage. Here, the salesperson presents a formal demonstration tailored to the prospect’s specific requirements. Involving an expert in the pitch can answer technical questions.
At this stage, the importance of selecting leads to pitch to becomes clear. Salespeople’s time is precious, and they should spend it on prospects with a real potential for conversion.
Handling objections: addressing concerns
Prospects may hesitate for various reasons, such as cost, timing, or fear of change. The objections stage is dedicated to addressing these hesitations. The aim is to show the value of your solution and the risks associated with not choosing it.
Preparing for common objections and developing empathetic responses is crucial for nudging prospects toward a decision.
Closing: finalizing the agreement
The closing stage aims to conclude a mutually beneficial deal. This results in a sale and involves a commission for the salesperson. The account is then transferred to an account manager for onboarding.
Follow-up: keeping the connection alive
After closing a sale, the salesperson’s job isn’t over. Maintaining communication is crucial for providing post-sales support. It can help you explore further sales opportunities and ask for referrals.
The follow-up stage focuses on reinforcing the relationship and ensuring customer satisfaction. This engagement keeps the brand at the forefront of the customer’s mind for the future.
How to improve your sales process

A flexible sales process is key to adapting to changing needs and goals over time. It’s crucial to acknowledge that methods that were effective in the past may not yield the same results today.
There’s no need to completely overhaul your process’s basic structure or complicate it further. Instead, focus on examining each stage to increase its effectiveness.
To improve your sales process, it’s recommended to follow these best practices:
Define goals and objectives at each sales process stage
Every sales process stage needs clear goals and objectives, with specific criteria for advancing a lead to the next stage. The stages should reflect the customer’s key buying decision phases. To set the right advancement criteria, look for verifiable signs of the customer’s willingness to move forward.
Assess if your sales process matches your ideal buyer’s discovery and purchase journey. Understanding their challenges and the solutions they seek is crucial. This finding allows you to tailor your sales process. It gives your team the tools to connect with buyers and customize your offerings.
Evaluate your current sales process.
To enhance your sales process, start by evaluating its current state. Ask yourself if you need to add or remove steps or if certain stages are too time-consuming. Reviewing past deals can offer insights into how your sales process has been executed and where it can be improved.
Understand your competition
Understanding your competition is vital for carving out your niche in the industry. It opens up opportunities to develop strategies that set you apart from competitors, improving your chances of attracting new customers.
Research brands that offer similar products or services. Focus on those targeting the same audience and locations as you. Examine their pricing, product advantages, social media presence, and website usability.
This analysis can reveal which strategies work well and show what you can adopt or avoid in your own sales approach.
Automate repetitive tasks
Consider automating the repetitive tasks within your sales process to increase efficiency. Sales automation tools can simplify and speed up your sales cycle.
Through automation, you can set workflows, send timely follow-up emails, update deal stages, and nurture relationships with automated greetings. Automating lead assignment and outreach ensures that all potential customers are engaged, making your sales pipeline more effective.
Monitor sales performance
Regular monitoring of your sales performance is key to growth. Automation tools provide detailed reports, helping you forecast revenue and assess sales performance. This information is essential for fine-tuning your sales strategies and recognizing the contributions of high-performing reps.
Gathering customer feedback
Customer feedback is invaluable. Surveys and feedback invitations give customers a chance to share their experiences. This feedback, combined with your sales data, can pinpoint where your sales process excels and where it needs improvement. Adjustments to your sales pitch, product specifications, or buying process, informed by customer insights, can boost satisfaction and attract new leads.
Identify and address bottlenecks.
Understanding your sales pipeline is necessary to spot where deals get stuck. Identifying these bottlenecks allows for targeted interventions to ensure a smoother sales pipeline. It is crucial to keep a constant eye on your sales process for real-time optimization. Tracking your sales process helps uncover any obstacles that need addressing. It ensures the process remains effective and responsive to changes.
Sales process template/flowchart
A sales process flowchart acts as a visual guide. It illustrates a salesperson’s steps to progress a lead from prospect to customer. It stands out from other documents by incorporating yes/no scenarios. These scenarios dictate specific actions based on the customer’s responses.
You can design this flowchart to ensure customers receive a consistent experience. It lists the necessary steps sequentially and highlights the main activities required at each stage.
Flowcharts can vary in complexity. They can either present a straightforward overview of the sales process from beginning to end or detail complex scenarios.
The stages included in a sales process flowchart could be:
- Lead Qualification Stage: The goal here is to determine if the lead fits your product or service.
- Preparation Stage: At this stage, you collect information about the customer and prepare a sales strategy tailored to them, assembling resources like product sheets.
- Approach Stage: The salesperson makes the first contact, delivering their pitch or arranging a meeting.
- Presentation Stage: You showcase your products or services to the customer engagingly.
- Handling Objections Stage: This involves addressing any reservations or objections from the customer.
- Closing Stage: Finally, you review the sale terms, confirm customer details, and complete the sale agreement.
This structured approach helps sales teams navigate the sales process. It also ensures a uniform and positive experience for the customer.
How to create a sales process

Building a sales process means examining each step as it happens. You need to see how each step fits your business, sales team, and customers. This method uncovers inefficiencies and highlights what works. It ensures your sales strategy aligns with your business goals. This alignment helps you create a plan that improves daily sales and drives long-term growth.
Understanding the ‘why’ behind every decision in your sales process is important. This is because your sales process is crucial to your sales organization. It underpins all your team’s sales activities.
Now, let’s look at how to create a sales process:
Understand the customer
The sales process starts with the buyer in mind. Understanding the buyer is essential to creating an effective sales process. You need to design your sales strategy based on their goals, motivations, and needs.
This involves figuring out why the buyer is searching for a solution and why they consider your solution. Gathering insights involves talking to potential buyers and your sales team. It also involves doing industry research.
Assess current sales activities
Your sales team follows a set of sales activities, even without a formal sales process. The first step to creating a structured sales process is understanding these current activities. Meet with your sales team members to learn about the steps they take with leads. It’s important to see how they view the process and to use their language and methods in your formal process.
Work backward from your goal
To create the best sales process, start with the end in mind. Define what you want to achieve at the end of each stage. Goals might include shortening the sales cycle or increasing win rates. Reviewing the effectiveness of past steps and the time taken for each can help. Engage stakeholders to understand how each team can influence the steps and actions.
Set milestones
Once you define the stages of your sales process, it’s time to establish milestones within those stages. Milestones help track progress, such as determining the buyer’s stage or engaging with stakeholders. Evaluating each milestone’s importance helps in resource allocation. Ensuring salespeople aim for these milestones prevents skipping steps or premature actions.
Providing training on the sales processes you set
Turning an amateur into an expert is possible with the right training. Training your team on your sales process makes them more proficient. For example, teaching someone to be qualified in lead improves their efficiency in that area. A well-trained employee knows the best methods and how to apply them.
Try, test, and tweak
Put in place your sales process and then track its effectiveness. Your sales team should check what aspects are working, what aren’t, and how prospects react. Over time, this evaluation reveals strengths and areas for improvement. You can then fine-tune the process to achieve the desired results.
How to measure the success of your sales process
As your sales team accelerates the progression of prospects through your pipeline, your sales process will evolve. Monitoring its success is essential to refining your sales process effectively.
This monitoring ensures that your team’s efforts are well-coordinated and you reach your target audience.
Several key performance indicators (KPIs) can help you measure the success of your sales process:
- Percentage of Prospects Closing Post-Demo: This metric tracks how many prospects become customers after seeing a product demonstration.
- Prospect to Paying Customer Conversion Rate: It measures how your process converts prospects into paying customers.
- Average Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): This calculates the total value a customer is expected to bring to your company over the duration of their relationship.
- Lead Conversion Rate: This rate assesses how effectively leads are converted into customers. It is calculated by dividing the number of captured leads by the total number of visitors.
- Sales Cycle Length: This metric determines the average time to close deals. It’s derived by dividing the total number of days for all deals by the total number of deals.
- Year-Over-Year (YOY) Growth: This measures growth compared to the previous year. The calculation formula is [(current period value ÷ previous period value) – 1] x 100.
- Win Rate: This evaluates the success rate of closing deals. It’s calculated by dividing the number of deals closed by the total number of deals made.
Sales process vs a sales methodology
Although the two terms sound identical, they represent entirely different concepts, each with its process. Thus, it’s crucial not to confuse the two. A sales process involves a series of actions that salespeople take to capture leads, engage with them, negotiate, and close deals.
Sales methodology refers to salespeople’s approach to implementing the entire sales process. It also shows how this contributes to business growth. This methodology’s framework includes a set of tools and processes that a sales rep uses during the sales process.
Thus, the sales process outlines your team’s actions to turn a prospect into a lead. On the other hand, sales methodology deals with the framework of various sales strategies. Your team experiments with these before selecting the most effective approach.
Mistakes to avoid when developing a sales process

It’s important to avoid common mistakes to create an effective sales process. This action will benefit your team and customers.
Here are some key things you could fail to take account of:
Defining actions and triggers
Defining specific, concrete actions to move your business’s prospects from one stage to the next is essential. If these triggers are not identified, your sales team might misunderstand what works for prospects.
Once defined, document your sales process. Share and practice it with your team through role-play exercises to solidify valuable techniques from each step.
The importance of research
Successful sales depend on thorough research. Proper research lets you speak about your offering and its solutions. Lack of research can diminish prospects’ confidence in your product and business. Understand what you’re selling and your target audience before making a sales call. This preparation prevents mistakes and enables you to address unique challenges and value propositions.
Customizing the sales process
A one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t always work in sales. Each prospect is different, with varying requirements. A strategy effective with one prospect might fail with another. It’s crucial to document every sales process you develop.
This documentation helps identify the most successful approaches. Keep records of each experiment to learn and develop more effective sales processes.
Defining sales process stages
Effective marketing requires a clear plan. Determine the stages your prospect will go through to ensure a smooth process. Identifying actions and triggers at each step allows you to see where efforts are lacking.
Avoiding premature pitches
Many salespeople, eager to meet quotas, often skip initial qualifying steps and dive into sales pitches. This haste can lead to interactions with unqualified prospects who may not have the interest, budget, or authority to purchase.
Exploring different sales methodologies
Relying on a single methodology may yield results, but exploring various methods can improve your sales process. Don’t shy away from experimenting with different sales approaches. Adjust your methods based on your prospects’ changing preferences.
Aligning sales plays with the process
Creating a sales process without aligning sales actions is ineffective. Document each rep’s specific actions at every process step for future reference.
For instance, detail the email outreach steps required during the prospecting stage. Store these templates where the whole team can access them. This strategy ensures efficiency by integrating sales actions with the sales process.
Focusing on solutions, not features
Sales calls often focus on product features, but prospects seek solutions and value. Highlight your product’s benefits, prioritizing value delivery at every step of the sales process. Continue providing value even if a prospect seems unlikely to purchase, as long as your product meets their needs.
Asking the right questions
Focus on understanding the customer’s priorities and what they stand to gain or lose from the engagement. This approach shifts the conversation from price to the broader value and solutions you can offer. This allows for more successful outcomes.
Continuous process improvement
Your sales process should always be evolving. Regularly check its success and check in with your sales team for feedback. Continuous development and refinement of your sales process can streamline operations and improve customer interactions.
Overcoming common objections
Prepare for potential objections by mapping out likely challenges and crafting empathetic, impactful responses. Understanding common objections and how to address them is crucial for closing sales.
Aligning marketing and sales
Keep your marketing team informed about sales activities to support the sales process better. This alignment allows marketing to provide improved prospects and nurturing materials, enhancing the overall sales strategy.
Prompt follow-up
Quick follow-up after sales calls is crucial to maintain interest. Delays can cause the prospect’s interest to wane, making closing more challenging.
Measuring and adjusting
Failure to track sales metrics or KPIs can make your sales process less effective. After developing or adjusting your sales process, measure its success to understand what works well and what needs improvement. Use sales dashboards or CRM metrics to monitor and fine-tune your sales process as required.
The future of the sales process
Creating a sales process influences your sales team’s performance. Implementing such a process ensures your team operates from a unified and effective playbook.
This strategy allows sales reps to offer a consistent experience to all prospects and customers, regardless of stage in the sales cycle. Keep your customers in mind as you develop your sales process.
Top-performing sales teams use customer expectations to shape their processes, and the most successful sales strategies focus on fulfilling customer needs.
By placing the customer at the center of your process, you make your reps’ work easier and enable them to generate more revenue.
A clear and reliable sales process boosts the satisfaction levels of your sales representatives and customers. Adopting digital adoption tools can enhance your team’s use of technology during sales.
Such tools include training materials specific to each step of the sales process. It will also consider product walkthroughs that underline the importance of various stages and milestones. Lastly, it will have personalized content tailored to the team’s current stage in the sales cycle.