The term Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines.
These programmed devices can mimic cognitive functions like learning, problem-solving, and decision-making, which you typically associate with the human mind.
AI has become an integral part of the technology that you interact with daily. It enhances efficiency, automates tedious tasks, and brings sophisticated analytics to help you make informed decisions. A 2023 McKinsey survey found that 55% of businesses have adopted AI in some form.
Whether you realize it or not, AI influences the way you shop, how enterprises target you for marketing, and even how you are diagnosed and treated by doctors.
The impact of AI in the workplace stretches far and wide, altering industries and shaping the future. According to research from PWC, AI will boost the global economy by $15.7 trillion by 2030.
But AI is not a monolith.
There’s a rich spectrum of types of AI, each of which has unique properties, strengths, and purposes.
Throughout this article, we’ll explore the various classifications of AI, from narrow, specialized systems that handle specific tasks, to the more advanced notion of superintelligent AI that outperforms human cognitive abilities.
Each type holds its unique set of capabilities and poses different implications for the future.
Understanding these distinctions will give you a clearer picture of AI’s role in both current and future technologies, and help you make the most of AI while mitigating the risks.
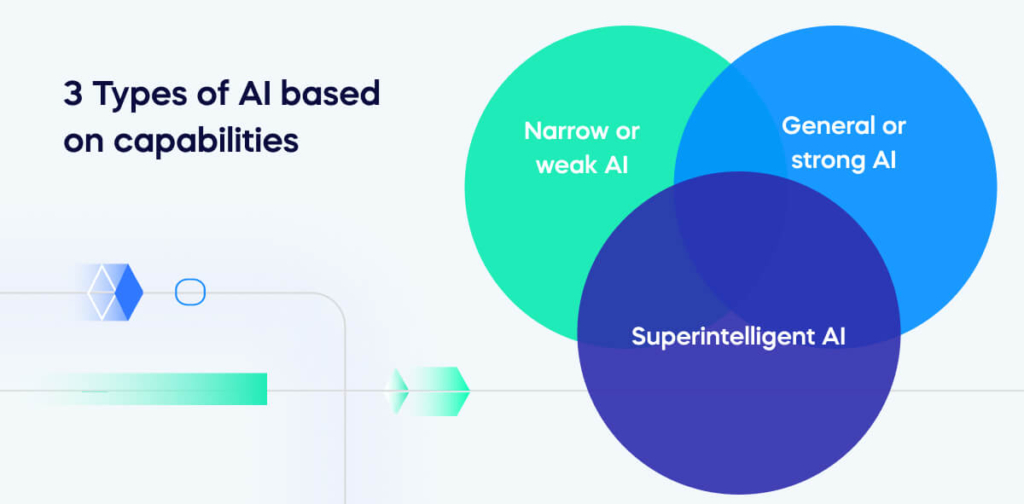
3 Types of AI based on capabilities
From tools that simplify your daily tasks to hypothetical constructs that challenge the boundaries of current science, AI manifests in various levels of complexity and potential.
In this section, we’ll delve into the capabilities of AI, breaking down the concept into three distinct categories:
- Narrow or weak AI – a specialized form of AI used for specific tasks.
- General or strong AI – AI developed and used to mirror human cognitive abilities.
- Superintelligent AI – a futuristic notion that envisions AI surpassing human intelligence.
Let’s explore each category to better understand the breadth and depth of AI’s capabilities:
Narrow or weak AI
You encounter narrow AI, also known as weak AI, in systems designed to perform specific tasks without the full range of human cognition.
These systems operate under a limited pre-defined range or set of behaviors and don’t possess consciousness, emotion, or genuine understanding. They are programmed to respond to certain stimuli in predictable ways.
Every day, you likely interact with narrow AI applications without even noticing. The personalized recommendations you see on e-commerce sites, the voice assistant on your phone, and the spam filter in your email are all examples of narrow AI.
General or strong AI
General AI, or strong AI, refers to a type of AI that can understand, learn, and apply its intelligence broadly, much like a human.
Unlike narrow AI, strong AI can solve unfamiliar problems with reasoning and is self-aware.
As of now, general AI remains largely theoretical; but, research is making strides, particularly in areas like natural language processing and autonomous decision-making.
Breakthroughs in these fields could pave the way for machines that learn and reason across various domains, transforming the AI landscape.
Superintelligent AI
Superintelligent AI takes the concept of general AI a step further.
It’s an AI that not only mimics human intelligence but significantly surpasses it in all aspects—creativity, general wisdom, and problem-solving.
This type of AI would be capable of extraordinary cognitive feats that humans could not achieve. Today, superintelligent AI is purely hypothetical and subject to much debate.
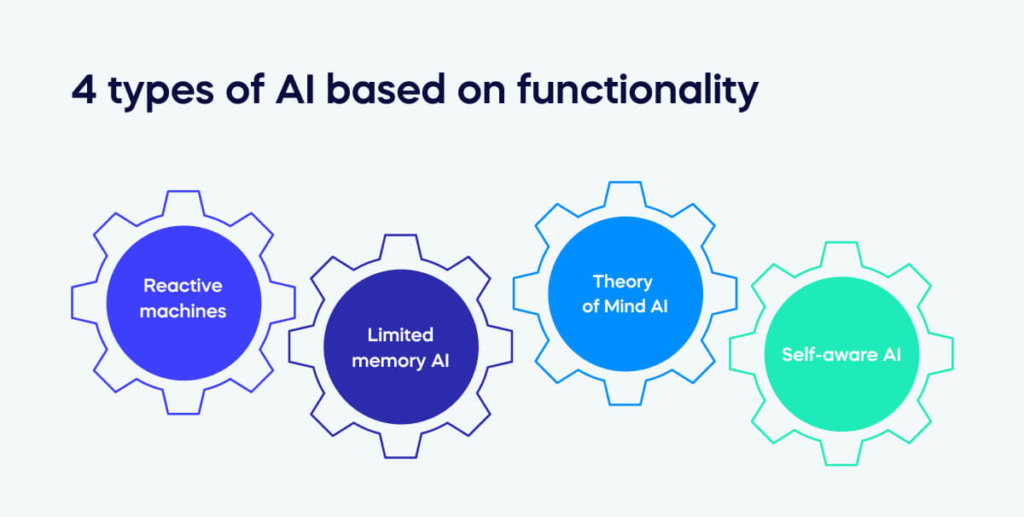
4 types of AI based on functionality
Another way you could differentiate different artificial intelligences is to look at the functional behavior of AI systems—how they perceive, react, learn, and potentially understand or interact with the world around them.
In simpler terms, it’s about what these AI systems can do and how they do it:
Reactive machines
These are the most basic forms of AI, designed to respond to specific situations or stimuli without any memory of past experiences.
They function by reacting to inputs with predetermined outputs, like a chess-playing AI that can’t learn from past games.
Limited memory AI
This type involves AI systems that can use recent or short-term data to make decisions.
Unlike reactive machines, they have a temporary memory, which allows them to adapt their responses based on recent information, like a self-driving car adjusting its actions based on recent traffic data.
Theory of Mind AI
This more advanced form of AI, still largely theoretical, would be capable of understanding and interpreting human emotions, beliefs, and intentions, and then responding in a contextually appropriate manner.
It’s about AI that can function in social contexts in a way that shows an understanding of human psychological states.
Self-aware AI
This is a hypothetical, future form of AI that would possess its own consciousness and self-awareness.
Such AI would not only understand its environment and interact intelligently but also have an understanding of itself as an entity—its own thoughts, feelings, and desires.
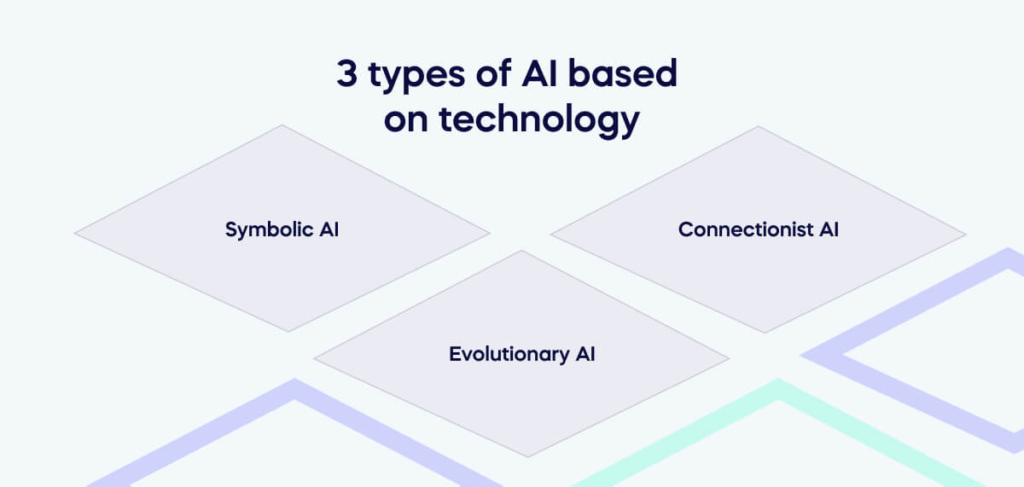
3 types of AI based on technology
When exploring artificial intelligence through the lens of technology, we focus on the underlying mechanisms and computational models that drive AI systems.
From rule-based systems to advanced neural networks, the technology behind AI defines both its capabilities and its potential for future evolution.
Symbolic AI
Symbolic AI operates on the principles of logic and rules.
This type of AI uses symbols to represent problems and applies a set of predefined rules to manipulate these symbols and derive conclusions or actions.
It’s akin to solving problems using a complex flowchart, where each decision leads to a specific outcome based on rules.
Connectionist AI
Connectionist AI, using artificial neural networks, simulates the human brain’s structure to learn and make decisions by analyzing data, identifying patterns, and making inferences.
This approach contrasts with Symbolic AI’s rule-based system, offering adaptability and proficiency in handling complex, real-world situations.
Connectionist AI is the foundation of most modern AI advancements, including progress in natural language processing, image and speech recognition, and predictive analytics.
Its learning capability has made it central to cutting-edge AI applications, driving much of the field’s current excitement and investment.
Evolutionary AI
Inspired by biological evolution, Evolutionary AI employs algorithms that mimic natural selection processes.
These algorithms use mutation, crossover, and selection to evolve solutions over generations.
They start with random solutions and iteratively evolve these towards better performance, guided by a fitness function.
Evolutionary AI’s innovations are diverse but useful in optimizing systems and evolving designs for complex problems. It thrives in environments with vast, ambiguous solution spaces, useful in robotic control, game strategy, and optimization challenges.
Its adaptability and creative problem-solving approach make it a valuable tool for tackling multifaceted issues.
Practical applications of different AI across industries
The real-world applications of AI are as varied as the types of AI themselves, demonstrating a profound impact across multiple sectors.
AI has proven to be a practical tool for driving innovation and efficiency.
Here’s a look at how different types of AI are being used in various industries:
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, AI is revolutionizing the way care is delivered.
AI-driven systems are being used for more accurate diagnoses, often identifying conditions from images like X-rays and MRIs with a precision that matches or exceeds that of human experts.
In treatment planning, AI algorithms can analyze data from numerous cases to suggest personalized treatment plans for patients, considering factors that might be overlooked by humans.
Moreover, AI is at the forefront of personalized medicine, tailoring healthcare to the individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors.
Finance
The finance industry has embraced AI for a range of applications.
AI systems are instrumental in detecting fraudulent transactions by analyzing patterns and identifying anomalies that deviate from usual behavior.
In trading, AI algorithms can process vast amounts of market data to identify trends and execute trades at optimal times, often faster than human traders could manage.
Risk analysis is another area where AI excels, helping financial institutions assess the creditworthiness of borrowers and the risk levels of various investment options by analyzing complex datasets.
Manufacturing
AI’s role in manufacturing is multifaceted, significantly boosting efficiency and productivity.
Predictive maintenance, powered by AI, can forecast equipment malfunctions before they occur, reducing downtime and repair costs.
In supply chain optimization, AI algorithms analyze various factors like market demand, weather, and logistics to optimize inventory levels and delivery routes.
Quality assurance also benefits from AI, with systems capable of inspecting and identifying defects more accurately and consistently than human inspectors.
Retail
The retail sector uses AI to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 customer service, handling inquiries and resolving issues promptly.
In product recommendation, AI algorithms analyze consumer behavior and preferences to suggest items, increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, AI plays a crucial role in inventory management, forecasting demand to optimize stock levels and prevent overstocking or stockouts, and ensuring that products are available when and where customers need them.
The future of AI types and their potential evolution
As AI continues to evolve and integrate into various aspects of life and industry, its future trajectory promises even more transformative changes.
In the future, a key development in AI could be the merging of different types, blending the strengths of narrow AI, general AI, and other forms for more sophisticated and versatile applications.
This convergence could lead to systems that not only excel at specific tasks but also adapt to new challenges and learn from a wider array of experiences.
For instance, combining the data processing power of narrow AI with the adaptive learning abilities of general AI could revolutionize fields like personalized medicine, where AI could diagnose, suggest treatments, and even predict future health issues based on a patient’s unique medical history.
That said, as AI becomes more advanced and widespread, security risks and ethical considerations will become increasingly complex and critical.
Issues such as data privacy, bias in AI decision-making, the impact of AI on employment, and the moral status of advanced AI systems will require careful navigation.
Establishing robust ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks will be essential to ensure that AI development is aligned with human values and societal well-being.
That means not just preventing harm but also addressing questions of fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI systems. The future of AI is not just about technological advancements but also about how these technologies are integrated into the fabric of society. Balancing innovation with ethical responsibility, and harnessing AI’s potential to address pressing global issues, will be key to shaping a future where AI contributes positively to human progress.

FAQs
Regulation tightens as AI becomes more autonomous: narrow AI requires basic data oversight; adaptive or generative AI demands stronger explainability, bias mitigation, and governance frameworks.
Evolutionary AI excels in design and optimization—like supply chain routing or configuration challenges—offering innovative, data-driven enhancements that static rule-based systems can’t achieve.
Upgrade to connectionist or adaptive AI architectures that can leverage broader historical context, unlock predictive insights, and respond dynamically to evolving data streams.
Reactive AI suits high-speed, low-complexity tasks—like fraud detection or automated alerts—where immediate rule-based responses are enough and broader context isn’t required.

