What is an IT roadmap?
An IT roadmap is a visual presentation of a technology strategy and supports the planning and execution of an IT strategy.

Table of contents
Roadmaps do not include all the information from a strategy. Instead, an IT roadmap highlights the most important elements of the organization’s technology plans.
As a result, an IT roadmap is an accessible visual representation that can create conversation, discussion, and clarification of a strategy.
IT roadmaps link together many aspects of a project in a simple format. That might be:
- The different stages involved in product development, service planning, or other tasks
- The different influences on the use of technology, such as resources available, business objectives, and wider forces of culture and society
- The causality, progression, timing, and sequence of all of these
- Wider business factors, such as staffing, budgets, vendors, and partners
Putting all these elements in one document helps stakeholders understand the processes ahead. In a recent Forbes article, Kim Huffman explained that it has a strategic role and can be a source of truth that department heads can use to help set their own goals.
Why is an IT Roadmap Important?
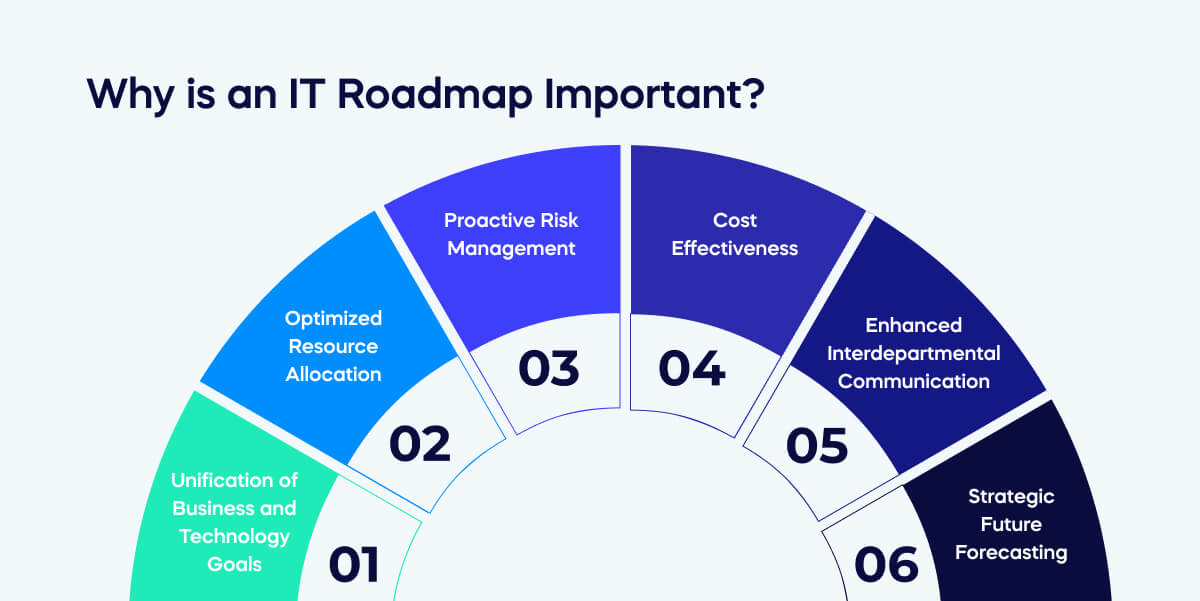
The importance of IT roadmap should not be underestimated.
It’s often your key go-to resource to ensure your company’s technological initiatives are aligned with your overall business goals.
An IT Roadmap plays a pivotal role in an organization’s strategic planning for several key reasons:
- Unification of Business and Technology Goals: An IT Roadmap aligns the technological initiatives with the wider organizational objectives. It ensures that every investment in technology contributes effectively towards accelerating business growth.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: A well-structured IT Roadmap aids in efficiently planning and managing resources. This includes tangible assets such as hardware and software and intangible resources like human capital.
- Proactive Risk Management: An IT Roadmap, acting as a risk mitigation tool, enables early identification of possible technological challenges and assists organizations in preparing and addressing risks linked to the deployment and utilization of technology.
- Cost Effectiveness: With a comprehensive IT roadmap, organizations can avoid redundant or unnecessary expenses, achieving greater cost efficiency.
- Enhanced Interdepartmental Communication: An IT Roadmap is a communication tool bridging the gap between IT and other business units. It provides a transparent overview of the IT department’s current projects and future plans.
- Strategic Future Forecasting: IT roadmaps provide insight into emerging technology trends and outline how they can be integrated into the existing business strategy to drive innovation and competitive advantage.
IT roadmap, IT strategic plan & IT framework: What’s the difference?
Understanding the key differences between an IT roadmap, an IT strategic plan, and an IT framework is important. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to different aspects of managing technology within an organization.
Let’s take a closer look:
IT Roadmap
An IT roadmap is a visual representation that outlines the strategic direction of technology investments that support the overall business strategy. It indicates what IT initiatives are in progress or planned, their timelines, and how they align with business objectives. Unlike an IT strategic plan, a roadmap focuses more on specific projects and timelines.
IT Strategic Plan
An IT strategic plan is a document that defines the strategy through which an organization can effectively use IT to achieve its business goals. It identifies key IT initiatives and projects based on the organization’s strategic goals. Unlike an IT roadmap, a strategic plan focuses more on the strategic direction and less on specific timelines or projects.
IT Framework
An IT framework refers to a set of guidelines that can be used to manage and govern IT services. It provides a structured and standardized approach to achieving IT and business goals. Unlike an IT roadmap or strategic plan, a framework is less about specific initiatives or strategies and more about providing a structure for managing and governing IT services.
What are the benefits of an IT roadmap?
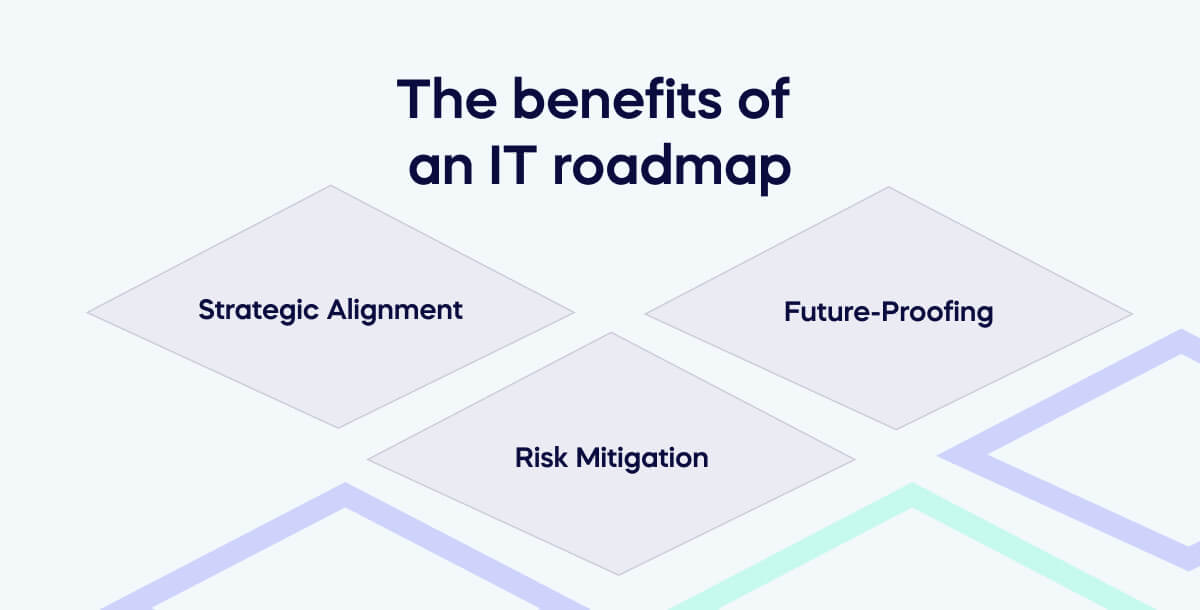
The benefits of an IT roadmap are numerous and can greatly impact the success of an organization.
The benefits of an IT roadmap include:
Strategic Alignment: Driving Business Objectives with Technology
An IT Roadmap is a critical tool that aligns strategically with technological initiatives and overarching business goals. It offers a coherent perspective on how each technological investment aligns with, supports, and drives the company’s strategic objectives. This guarantees that technology acts as a catalyst to propel the organization toward its targets rather than being a standalone entity.
Future-Proofing: Staying Ahead of the Technological Curve
The IT Roadmap is instrumental in preparing businesses for future technology needs and trends. The ability to anticipate, plan, and seamlessly integrate new technologies into existing systems is crucial for staying competitive. A well-defined roadmap ensures the organization is not just reacting to changes but is prepared and equipped to leverage emerging technologies for business advantage, thereby future-proofing the organization.
Risk Mitigation: Early Identification and Management of Technological Risks
An IT Roadmap serves as a proactive risk mitigation strategy. Organizations can devise effective countermeasures by facilitating early identification of potential technological challenges. This reduces the likelihood of unexpected setbacks during technology deployment and usage, ensuring smoother transitions and minimizing potential disruptions to business operations.
How to create an IT roadmap
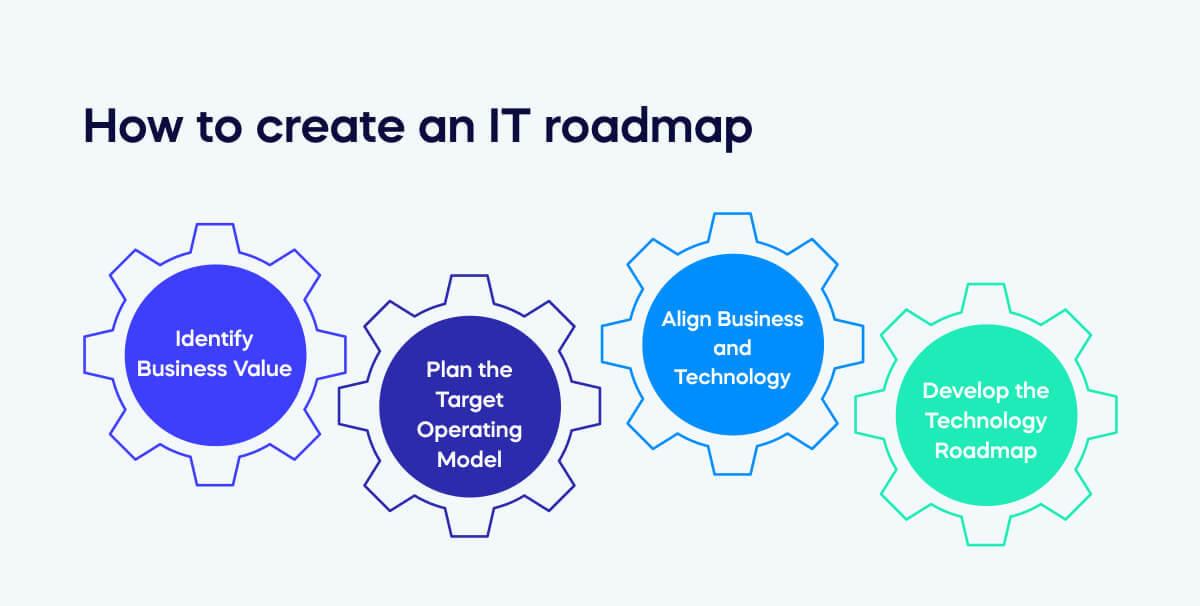
A well-crafted IT roadmap isn’t just a plan—it’s a compass.
It navigates the complex terrain of tech initiatives, aligning them with business goals and ensuring they don’t veer off course. It’s a critical tool in the arsenal of any organization seeking to leverage technology for growth.
Creating an IT roadmap is like constructing a bridge between your current IT landscape and your future aspirations. This involves prioritizing projects, defining actions, setting timelines, and adapting to the ever-changing tech landscape.
Let’s delve into the art and science of crafting a robust IT roadmap.
Step 1: Identify Business Value
The journey begins by understanding the potential business value of the digital transformation. Start by building a high-level business case, quantifying the transformation’s value objectively. This involves a hypothesis-driven approach to uncover key value levers, such as automation and simplification, while assessing the implementation costs. Correctly identifying business value sets the foundation for the entire transformation strategy.
Step 2: Plan the Target Operating Model
Once sources of business value are known, design the target operating model from the ground up. This model should leverage digital capabilities and incorporate all transformation initiatives, including quick wins. Identify major pain points, set priorities among functions, and guide the new model with key performance indicators. Ensure sustainable change management by centralizing efforts in a transformation office.
Step 3: Align Business and Technology
Align business and technology by assessing the organization’s technology landscape and planning the technology roadmap. Evaluate architectural decisions against best-practice reference architectures, define IT-enablement requirements, and consider the implications of improvement levers. Design the new architecture by linking business strategy, processes, and IT teams, then create a transformation roadmap aligned with the overall company strategy.
Step 4: Develop the Technology Roadmap
Assess the technology landscape and define IT-enablement requirements for the target-state operating model. Evaluate architectural decisions against best-practice reference architectures and map the interdependencies of improvement levers. Create a transformation roadmap aligned with the overall company strategy, integrating business and technology elements.
IT Roadmap business use cases
The concept of an IT roadmap has diverse use cases across industries.
IT roadmaps can be especially useful in digital change management projects. However, they can alternatively be used for forecasting purposes.
Here are a few examples of IT roadmap use cases:
- In a technology company, an “IT roadmap” (or “technology roadmap”) could be related to the specific challenges involved in developing a particular type of technology, whether it’s software or hardware.
- In manufacturing, IT and technology have a serious impact on business outcomes. A roadmap can help understand the forthcoming opportunities and challenges in a business.
- For white-collar businesses, an IT roadmap might apply to many aspects of digital transformation, as a 2020 McKinsey analysis usefully explains.
Different types of IT roadmaps offer valuable insights into the complexities of implementing and leveraging significant changes. For example, these may include an IT infrastructure roadmap, a cloud roadmap, and an ERP implementation roadmap.
IT roadmap formats
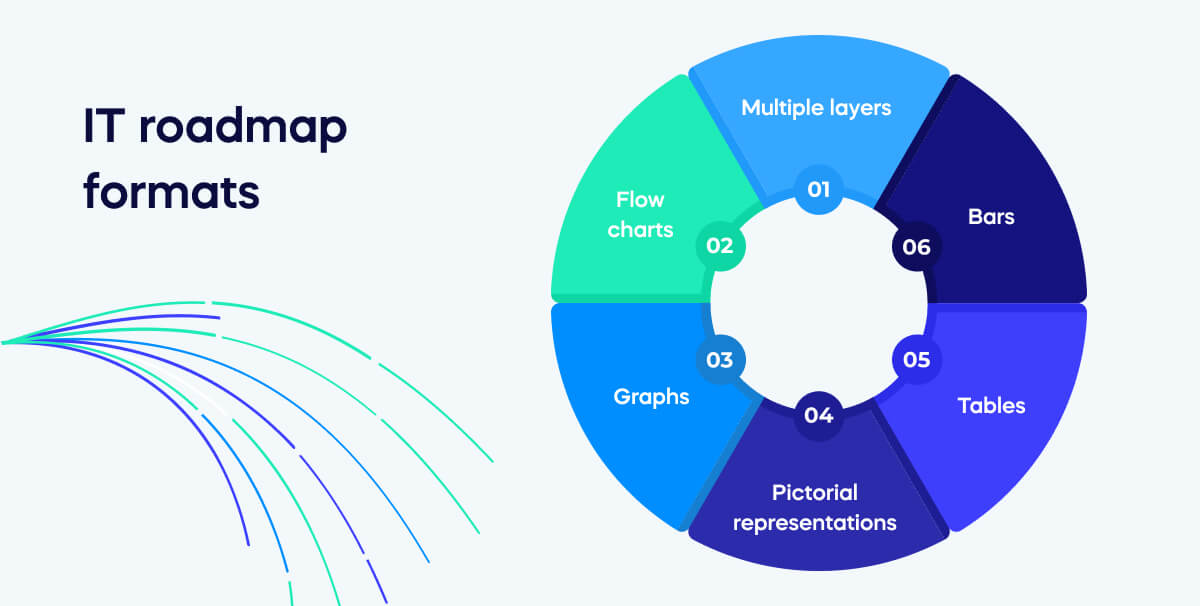
Once you’ve decided on your use case, the next step is determining what it will look like.
Here are some common formats for presenting IT and technology roadmaps:
- Multiple layers. Divide the roadmap into different layers or sections to represent different aspects of the IT strategy or project.
- Bars. Use bars to indicate project timelines, milestones, or phases. Gantt charts are a common example of using bars.
- Tables. Present tabular data for detailed information, such as resource allocation, budgets, or project dependencies.
- Graphs. Incorporate graphs to visualize data trends, performance metrics, or key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Pictorial representations. Use images, icons, or symbols to represent concepts, technologies, or project components.
- Flow charts. Create flowcharts to illustrate process workflows, decision trees, or the sequence of tasks and activities.
Each project requires a unique combination of formats to communicate all the necessary details effectively. The key is to find what works best for your specific project.
IT Roadmap examples
IT roadmaps are a highly flexible format. The single idea of a “roadmap” takes many different forms. Understandably, some people look for roadmap templates, but whatever design you choose, you’ll need to adapt it to the very specific requirements of your project.
In this section, we will take a look at three major roadmaps:
Gartner’s 2023 Technology Adoption Roadmap in data and analytics –
Gartner’s 2023 Technology Adoption Roadmap for Data and Analytics roadmap offers valuable insights for D&A leaders.
The visual roadmap highlights key technology trends, adoption challenges, and deployment timelines for 38 emerging D&A technologies.
It underscores the importance of piloting technologies to meet business expectations, addresses talent challenges, and emphasizes the strategic focus on foundational initiatives and AI.
The roadmap guides leaders in prioritizing user-focused technologies, investing in cutting-edge D&A architecture, and focusing on platforms that deliver end-to-end governance for successful business outcomes.
The visual representation enhances decision-making by providing a clear and concise overview of the D&A landscape.
IBM roadmap for scaling quantum technology
IBM’s quantum technology roadmap serves as a crucial guide, illustrating the evolution of quantum processors and emphasizing IBM’s commitment to overcoming challenges in quantum computing, such as prolonged control of large qubit systems with minimal errors.
It charts the progression of quantum processors and underscores IBM’s broader mission: designing a full-stack quantum computer accessible worldwide via the cloud.
The roadmap is a testament to IBM’s dedication to continuous improvement, incorporating lessons from smaller devices into an aggressive scaling strategy for larger systems.
It acts as a navigational tool, guiding IBM through the intricacies of quantum development and positioning them for transformative breakthroughs in the coming decade.
Intel’s Leaked 2022 roadmap
A leaked roadmap from Intel shows their hopes of outperforming Apple’s M1 Max with a new Arrow Lake processor by late 2023 or early 2024.
A leaked slide suggests Intel’s focus on achieving this goal, targeting premium designs and emphasizing high-performance collaboration. While Intel aims for efficiency gains, plans may evolve.
What comes after an IT Roadmap?
Post-execution of an IT roadmap, optimization becomes the strategic priority.
This involves refining workflows, reallocation of resources, or further technological investments to enhance productivity. Successful strategies should be scaled across other departments or projects to maximize their impact.
The concept of continuous improvement is integral as technology and business needs evolve. Regular assessments and revisions of the IT roadmap are necessary to ensure alignment with organizational goals and current tech trends.
Maintaining open lines of communication with stakeholders about changes, results, and future plans is vital. Insights gleaned from the current IT roadmap should inform the planning for the next iteration, addressing new goals or challenges that have emerged.
Thus, the process calls for an ongoing cycle of planning, execution, evaluation, optimization, scaling, and reiteration.