What is a self-service portal?
A self-service portal is a digital platform or interface that allows individuals to independently access and manage various services, information, or resources without direct human intervention.

Table of contents
- What is a self-service portal?
- Why are self-service portals important?
- How WalkMe’s self-service portal overcomes challenges
- Use cases for self-service portals
- Examples of self-service portal success
- Advantages of self-service portals
- Challenges of self-service portals
- Empowering change: The strategic role of self-service portals in digital transformation
It empowers users to perform tasks, gather information, and complete transactions independently, increasing efficiency and convenience.
Like digital transformation, which integrates advanced digital tools into organizational workflows, a self-service portal leverages technology to streamline and enhance user interactions with services or systems.
It often provides a user-friendly interface, enabling individuals to access relevant information, submit requests, perform transactions, and find solutions to their queries independently.
In essence, a self-service portal is a key component of modern organizational practices that aims to empower users, improve operational efficiency, and enhance overall user experience by putting control and accessibility in the hands of the end-users.
Embracing a self-service portal in business streamlines operations, enhances user experiences, and serves as a catalyst for propelling the workforce forward.
By empowering employees with tools to independently access information, submit requests, and navigate processes, the self-service portal fosters a culture of self-sufficiency, promoting efficiency, agility, and continual improvement within the organizational framework.
Why are self-service portals important?
A self-service portal is crucial for organizations as it empowers users to access information and services independently, reducing dependence on manual interventions and fostering operational efficiency.
Furthermore, it enhances user satisfaction by providing a seamless, convenient, and personalized experience, contributing to increased productivity and streamlined business processes.
Benefits of WalkMe’s self-service portal
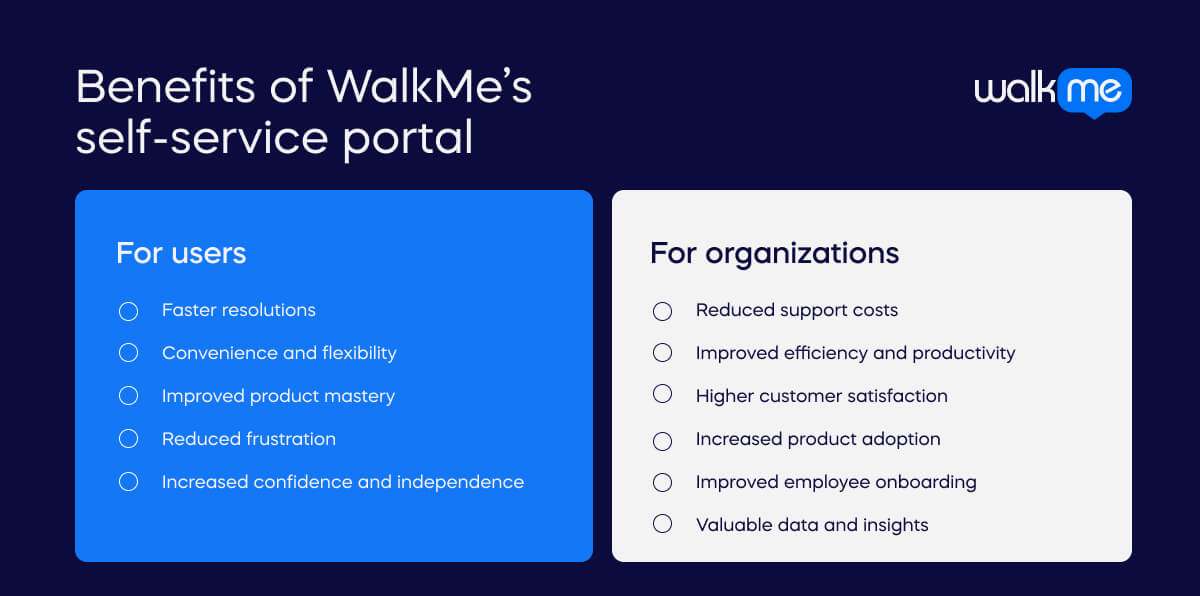
WalkMe’s self-service portal offers a range of benefits for both users and organizations:
For users
- Faster resolutions: Users can find answers to their questions and solve problems quickly and easily without waiting for support tickets or calls.
- Convenience and flexibility: Users can access the portal 24/7 from any device, allowing them to find help when needed.
- Improved product mastery: The portal provides clear and concise instructions, walkthroughs, and tutorials, helping users learn the platform more effectively and unlock its full potential.
- Reduced frustration: By empowering users to find solutions independently, the portal can help reduce frustration and improve the overall user experience.
- Increased confidence and independence: With access to readily available resources, users can feel more confident and independent in navigating the platform.
According to Gartner, many customers prefer digital and self-service over assisted-service channels because they are always available and eliminate wait time for an agent.
For organizations
- Reduced support costs: By deflecting support tickets and calls, the portal can help reduce the workload on support teams and lower overall support costs.
- Improved efficiency and productivity: By enabling users to solve problems on their own, the portal can free up support teams to focus on more complex issues and improve overall efficiency.

In December 2021, Gartner surveyed 400 finance executives and found that self-service data and analytics were seen as a driver of employee productivity by 49% of respondents.
- Higher customer satisfaction: By providing a convenient and effective self-service option, the portal can help to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased product adoption: The portal can help drive the adoption of new features and functionality by providing users with easy-to-follow guidance.
- Improved employee onboarding: The portal can create guided employee onboarding, helping them learn the platform quickly and effectively.
- Valuable data and insights: The portal can provide valuable data and insights into user behavior, which can be used to improve the platform and the self-service experience.
How WalkMe’s self-service portal overcomes challenges
Traditional self-service portals often face challenges hindering their effectiveness and user adoption.
WalkMe’s self-service portal tackles these challenges through several innovative features and approaches:
Overcoming information overload
- Contextual guidance: WalkMe integrates directly into the platform’s interface, providing help precisely where users need it, eliminating the need to search through mountains of documentation.
- Personalization: Based on user roles, needs, and usage history, WalkMe tailors the information displayed, avoiding overwhelming users with irrelevant content.
- Microlearning: WalkMe breaks down complex tasks into bite-sized, digestible steps, making it easier for users to absorb information and avoid cognitive overload.
Engaging users and driving adoption
- Interactive walkthroughs: WalkMe’s interactive guides walk users through tasks step-by-step, keeping them engaged and actively learning.
- Gamification elements: WalkMe incorporates gamification elements like badges and progress bars to motivate users to explore the portal and learn new things.
- Targeted nudges: Based on user behavior, WalkMe can trigger proactive prompts and suggestions, encouraging them to use specific features or access relevant resources.
Measuring and improving effectiveness
- Comprehensive analytics: WalkMe provides detailed analytics on portal usage, user behavior, and task completion rates, allowing organizations to identify areas for improvement.
- A/B testing: WalkMe’s A/B testing functionality enables organizations to test different versions of content and guidance to see which ones resonate best with users.
- Continuous feedback: WalkMe encourages user feedback through surveys and in-app tools, allowing organizations to gather valuable insights and refine the self-service experience.
Addressing these common challenges, WalkMe’s self-service portal fosters a customer-centric approach, resulting in higher adoption rates, improved satisfaction, and a more successful digital experience for both users and organizations.
Use cases for self-service portals
Unlocking convenience and efficiency, self-service portals are integral across diverse scenarios, revolutionizing how users interact with systems and services.
Self-service portals in business
Self-service portals find practical applications across various contexts, showcasing their versatility and effectiveness in streamlining processes.
Here are a few scenarios where self-service portals are actively utilized across different features and functionalities:
Customer support and issue resolution
- Users can submit support tickets, report issues, and access knowledge bases for self-help.
- Real-time status tracking keeps users informed about the progress of their requests.
Employee onboarding and HR services
- New employees can access onboarding materials, submit documentation, and complete orientation tasks independently.
- HR services, such as leave requests, benefits enrollment, and payroll information, can be managed through the portal.
IT service management
- Users can initiate IT support requests, troubleshoot common issues, and access self-help resources.
- The portal often includes features for software installations, password resets, and hardware requests.
Self-service portal with WalkMe
WalkMe doesn’t just offer a standalone self-service portal; it seamlessly integrates self-service capabilities into its core features and functionalities, creating a powerful synergy:
Contextual guidance
- Walkthroughs: Embed self-service content directly within WalkMe’s step-by-step walkthroughs. Imagine a walkthrough explaining a complex feature with a link to a relevant FAQ within the same step, providing immediate context-sensitive help.
- WalkThru bubbles: Leverage WalkMe’s signature bubbles to trigger self-service content like video tutorials or knowledge base articles based on user actions or specific UI elements.
- Dynamic overlays: Use WalkMe’s overlays to display dynamic self-service content like personalized tips, reminders, or announcements based on user data or real-time context.
Knowledge base integration
- Search integration: Allow users to directly search the self-service portal’s knowledge base within WalkMe, streamlining access to relevant information while navigating the platform.
- Targeted recommendations: Using the current walkthrough or user activity, WalkMe can suggest relevant knowledge base articles or FAQs, proactively delivering helpful information.
- Knowledge base walkthrus: Create interactive walkthroughs directly within the knowledge base, guiding users through complex procedures or troubleshooting steps.
User feedback and improvement
- Feedback buttons: Integrate feedback buttons within WalkMe’s elements to gather user input on the self-service content or specific features, closing the feedback loop and improving the portal’s effectiveness.
- Sentiment analysis: Analyze user interactions with WalkMe elements and self-service content to identify areas for improvement and personalize the overall experience.
- Usage data insights: Leverage WalkMe’s analytics to track user engagement with the self-service portal, identify frequently accessed topics, and optimize content accordingly.
Gamification and engagement
- Points and badges: Award points and badges for completing self-service portal activities like reading articles, providing feedback, conducting walkthroughs, driving engagement, and exploration.
- Leaderboards: Create leaderboards based on self-service portal activity, fostering friendly competition and encouraging knowledge sharing among users.
- Progress tracking: Allow users to track their progress through self-service learning modules or knowledge base sections, boosting motivation and a sense of accomplishment.
By combining WalkMe’s powerful guidance and engagement features with the self-service portal’s informative content and personalized learning, organizations can create a truly comprehensive and effective user experience that empowers users, optimizes resources, and drives platform success.
Examples of self-service portal success
Organizations have successfully leveraged self-service portals to revolutionize their digital adoption strategies. Here are some examples:
How businesses find success with self-service portals
Salesforce
A leader in CRM solutions, Salesforce employs a robust self-service portal to enhance its digital adoption strategy.
Customers can independently manage their accounts through the portal, access training resources, and troubleshoot common issues.
This approach has improved user experience by providing instant support and streamlined the customer support process, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Microsoft
The tech giant leverages a comprehensive self-service portal for IT service management, allowing employees to handle IT-related tasks independently.
From submitting support tickets to accessing knowledge bases for troubleshooting, employees can efficiently resolve issues without direct IT intervention.
This has resulted in increased productivity as employees experience reduced downtime, and IT resources can focus on more complex tasks, contributing to a more agile and responsive organization.
Amazon

This global e-commerce giant utilizes a feature-rich self-service portal to empower customers to manage their orders and accounts.
Users can track shipments, initiate returns, and customize preferences, providing a seamless and personalized experience.
This implementation has significantly improved user satisfaction, reduced customer support overhead, and created a more efficient order management system, ultimately contributing to Amazon’s dominance in the e-commerce industry.
Driving innovation with WalkMe
WalkMe’s self-service portal, when integrated with its core features, can deliver significant benefits in terms of streamlined processes, improved user engagement, and optimized workflows.
Here are some examples of the success companies have experienced with WalkMe’s solution:
Unity Technologies
Unity, a leading game engine developer, faced an influx of new users with varying skill levels, leading to high support ticket volume and onboarding inefficiencies.
The company implemented WalkMe with an integrated self-service portal. They created dynamic overlays and contextual walkthroughs that triggered relevant knowledge base articles and FAQs based on user actions.
They experienced the following benefits:
- 50% reduction in support tickets: Self-service content empowered users to find solutions independently.
- 25% faster onboarding: Interactive walkthroughs guided new users through essential steps, streamlining the process.
- 40% increase in platform adoption: Users explored more features with easier access to self-service resources.
DocuSign
DocuSign, a popular e-signature platform, needed to cater to diverse user needs across various industries and roles, leading to complex workflows and knowledge gaps.
The organization incorporated WalkMe’s self-service portal with personalized recommendations and dynamic content.
They used WalkThru Bubbles to offer contextual tips and video tutorials based on user roles and specific document types.
Here are some of the results they gained:
- 30% reduction in training time: Interactive walkthroughs replaced traditional training methods, saving time and resources.
- 20% increase in workflow efficiency: Personalized tips and guidance within tasks streamlined document processing.
- Enhanced user experience: Tailored self-service content catered to individual needs, reducing errors and frustrations.
Advantages of self-service portals

The advantages of implementing a self-service portal within an organizational framework are manifold, ushering in a range of benefits that contribute to enhanced efficiency, improved user experiences, and streamlined operations.
These advantages include:
Empowered user autonomy
Self-service portals empower users to independently access information, perform tasks, and find solutions, reducing dependency on manual assistance.
This autonomy enhances user satisfaction and fosters a culture of self-sufficiency, saving time for both users and support teams.
24/7 accessibility and convenience
Providing round-the-clock accessibility, self-service portals break free from time constraints, allowing users to engage with services or information at their convenience.
This meets modern consumers’ expectations and ensures uninterrupted service availability, especially for global or remote audiences.
Increased operational efficiency
By automating routine tasks and standardizing processes, self-service portals contribute to increased operational efficiency.
This efficiency is manifested through quicker service delivery, reduced manual errors, and optimized resource utilization, allowing organizations to allocate human resources to more strategic and complex endeavors.
Cost savings and resource optimization
Automating and reducing manual interventions achieved through self-service portals result in significant cost savings.
Organizations can allocate resources more efficiently, redirecting manpower to tasks that require a human touch while reducing the load on support teams for routine inquiries.
Challenges of self-service portals
While self-service portals offer numerous advantages, their implementation also comes with certain challenges that organizations must navigate effectively.
These challenges include:
User adoption resistance
Encouraging users to embrace self-service options can be challenging, as some individuals may resist change or prefer traditional modes of interaction.
Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication, training programs, and a user-friendly interface incentivizing adoption.
Content relevance and maintenance
Ensuring that the information available on the self-service portal remains current, accurate, and relevant is an ongoing challenge.
Regular updates, content audits, and a well-defined maintenance strategy are essential to prevent outdated information and to maintain the portal’s usefulness.
Empowering change: The strategic role of self-service portals in digital transformation
In the context of digital transformation, digital adoption, and change management, the self-service portal stands as a transformative force, serving as a strategic imperative that reshapes operational dynamics.
Positioned at the intersection of technology and user empowerment, self-service portals play pivotal roles in fostering efficiency, innovation, and continual improvement within organizations.
As a linchpin in digital transformation initiatives, self-service portals seamlessly integrate with advanced digital tools, transcending traditional implementation boundaries.
This integration enhances operational efficiency and empowers users to independently access information, initiate transactions, and manage processes.
The strategic emphasis on proficiency over mere familiarity positions the self-service portal as a catalyst for change, ushering in a user-centric era where autonomy and seamless interactions drive organizational success.